- Portal:Ancient Near East
-
- Wikipedia portals:
- Culture
- Geography
- Health
- History
- Mathematics
- Natural sciences
- People
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Society
- Technology
History: Ancient Egypt • Ancient Germanic Culture • Ancient Greece • Ancient Japan • Ancient Near East • Ancient Rome • Archaeology • Austria-Hungary • British Empire
 • Bulgarian Empire • Byzantine Empire • History of Canada • Imperial China • Classical Civilisation • Colonialism • Disasters • Heraldry • History of Science
• Bulgarian Empire • Byzantine Empire • History of Canada • Imperial China • Classical Civilisation • Colonialism • Disasters • Heraldry • History of Science • Indian independence movement • Khitan • Middle Ages • New France • Russian Empire • War
• Indian independence movement • Khitan • Middle Ages • New France • Russian Empire • War The Ancient Near East Portal
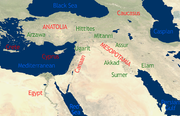
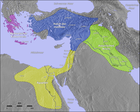
The Ancient Near East Portalrefers to early civilizations in a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq and Syria), Persia (modern Iran), Armenia, Anatolia (modern Turkey), the Levant (modern Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, and Jordan), and Ancient Egypt, from the beginnings of Sumer in the 6th millennium BC until the region's conquest by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC.
The ancient Near East is considered the Cradle of Civilization. It was the first to practice intensive year-round agriculture; it produced the first writing system, invented the potter's wheel and then the vehicular- and mill wheels, created the first centralized governments, law codes and empires, as well as introducing social stratification, slavery and organized warfare, and it laid the foundation for the fields of mathematics, medicine and astronomy.
Selected article[[Image:|140x170px|left|Main stairway at Persepolis palace]]The Achaemenid Empire (550 – 330 BC) was forged by Cyrus the Great, and became territorially the largest empire in antiquity, stretching from Pakistan and Central Asia to the Black sea, Asia Minor and Thrace, and much of Egypt going as far west as Libya. It is noted in western history as the foe of the Greek city states in the Greco-Persian Wars, for freeing the Israelites from their Babylonian captivity, and for instituting Aramaic as the empire's official language. This era saw the spread of Persian culture, and the beginning of the decline of ancient Near East culture centered in Babylon. Two centuries later, after Alexander the Great's conquest, Greece would eclipse both.
Selected biographyShamshi-Adad I (reigned c. 1745 ñ 1717 BC (short chronology)) rose to prominence when he carved out a large empire in northern Mesopotamia, founding the Old Assyrian Empire, although the Assyria was soon defeated by Hammurabi of Babylon and remained in the shadow of the Babylonian Empire throughout the "old Assyrian" period.Shamshi-Adad was a great organizer, keeping firm control on all matters of state, from high policy down to appointing officials and dispatching provisions. His campaigns were meticulously planned, and his army knew all the classic methods of siegecraft, such as encircling ramparts and battering rams. Spies and propaganda were often used to win over rival cities. However, his empire lacked cohesion and when news of his death spread, old rivals set out at once to topple his sons from the throne.
Selected pictureCredit: PHGCOM Goddess and Child Hittite, mid 2nd millennium BC (Metropolitan Museum) Did you know......that the Hurrian language and the Urartian language are proposed to be distantly related to the modern Armenian language?...that the Aramaic language, the lingua franca of the ancient Near East in Biblical times is still spoken as a first language today?
...that the syllabic cuneiform script was adapted to create a phonetic alphabet twice, for the Ugaritic language and for the Old Persian language?
Quality content Featured article: Sargon of Akkad
Featured article: Sargon of Akkad Good articles: Akkadian Empire • Hammurabi • Artaxerxes III Ochus • ZoroastrianismThings you can do
Good articles: Akkadian Empire • Hammurabi • Artaxerxes III Ochus • ZoroastrianismThings you can do- Add an {{ANE portal}} template to all articles that fall within the scope of this portal.
- Add a {{WP ANE}} WikiProject banner to their talk pages.
- Edit articles, create new articles, and expand stub articles:
- Clean up articles needing attention
- Improve articles to good article status.
- Maintain quality by monitoring recent changes.
- Make sure all pages have the templates in #1 above, for their recent changes to appear.
- Upload images to Wikicommons
See also resources for editors.Categories[×] HabiruRelated WikiProjectsAncient Near East • Archaeology • Languages • History • Military history • Mythology • Ancient Egypt
Assyria • Jewish history • Bible • ZoroastrianismCategories:- Ancient Near East portal
- History portals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.