- p-Xylene
-
p-Xylene 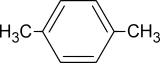
 Other namesp-Xylol
Other namesp-Xylol
1,4-DimethylbenzeneIdentifiers CAS number 106-42-3 
UNII 6WAC1O477V 
KEGG C06756 
ChEMBL CHEMBL31561 
RTECS number ZE2625000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC1=CC=C(C)C=C1
Properties Molecular formula C8H10 Molar mass 106.16 g/mol Appearance Colorless liquid
colorless crystalline solidDensity 0.861 g/mL Melting point 13.2 °C, 286 K, 56 °F
Boiling point 138.35 °C, 412 K, 281 °F
Solubility in water insoluble Solubility in ethanol very soluble Solubility in diethyl ether very soluble Refractive index (nD) 1.49582 Viscosity 0.7385 cP at 0 °C
0.6475 cP at 20 °CDipole moment 0.07 D Hazards MSDS External MSDS R-phrases R10 R20 R21 R36 R38 S-phrases S25 Main hazards Harmful or fatal if swallowed. Vapor harmful. Flammable liquid and vapor. NFPA 704 Flash point 25 °C Related compounds Related aromatic
hydrocarbonsbenzene
toluene
o-xylene
m-xyleneSupplementary data page Structure and
propertiesn, εr, etc. Thermodynamic
dataPhase behaviour
Solid, liquid, gasSpectral data UV, IR, NMR, MS  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references p-Xylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon, based on benzene with two methyl substituents. The “p” stands for para, identifying the location of the methyl groups as across from one another.
It is an isomer of xylene. Other isomers include o-xylene and m-xylene. p-Xylene is used on a large scale for the manufacture of terephthalic acid for polyester. Its polymer is known as Parylene. p-Xylene is produced by catalytic reforming of naphtha (a petroleum derivative) and separated in a series of distillation, adsorption or crystallization and reaction processes from m-xylene, o-xylene and ethylbenzene. Its melting point is the highest among this series of isomers, but simple crystallization does not allow easy purification due to the formation of eutectic mixtures.
References
External links

This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.

