- Moya (architecture)
-
 Yellow: moya, white: hisashi, red: mokoshi
Yellow: moya, white: hisashi, red: mokoshi
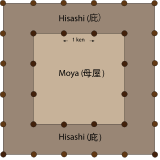
In Japanese architecture moya (母屋) is the core of a building. Originally the central part of a residential building was called moya. After the introduction of Buddhism to Japan in the 6th century, moya has been used to denote the sacred central area of a temple building. It is generally surrounded by aisle like areas called hisashi.[1] In temples constructed in the hip-and-gable style (irimoya-zukuri), the gabled part usually covers the moya while the hipped part covers the aisles.[2]
A butsuden's floor plan
The drawing shows the floor plan of a typical Zen main butsuden such as the one in the photo above at Enkaku-ji in Kamakura. The core of the building (moya) is 3 x 3 ken wide and is surrounded on four sides by a 1-ken wide hisashi, bringing the external dimensions of the edifice to a total of 5 x 5 ken.[3] Because the hisashi is covered by a pent roof of its own, the butsuden seems to have two stories, but in fact has only one.
This decorative pent roof which does not correspond to an internal vertical division is called mokoshi (裳階・裳層 also pronounced shōkai), literally "skirt story" or "cuff story".
The same structure can be found in a tahōtō with the same effect: the structure seems to have a second story, but in fact it doesn't.[4]
References
- ^ "moya". JAANUS - Japanese Architecture and Art Net User System. http://www.aisf.or.jp/~jaanus/deta/m/moya.htm. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ "irimoya-zukuri". JAANUS - Japanese Architecture and Art Net User System. http://www.aisf.or.jp/~jaanus/deta/i/irimoyazukuri.htm. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ "hisashi". JAANUS - Japanese Architecture and Art Net User System. http://www.aisf.or.jp/~jaanus/deta/h/hisashi.htm. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ Fujita Masaya, Koga Shūsaku, ed (April 10, 1990) (in Japanese). Nihon Kenchiku-shi (September 30, 2008 ed.). Shōwa-dō. ISBN 4-8122-9805-9.
Elements of Japanese architecture Styles Buddhist · Buke · Daibutsuyō · Gassho · Giyōfū · Hachiman · Hirairi · Hiyoshi (also called Hie) · Irimoya · Ishi-no-ma · Kasuga · Kibitsu · Nagare · Ōbaku Zen · Setchūyō · Shinden · Shinmei · Shinto · Shoin · Sukiya · Sumiyoshi · Taisha · Wayō · ZenshūyōA model of Himeji Castle
Building types Roof styles Structural Burdock piling · Chigi · Disordered piling · Engawa · Fusuma · Hisashi · Irimoya-zukuri · Irori · Jinmaku · Katōmado · Katsuogi · Kuruwa · Mokoshi · Moya · Nakazonae · Namako wall · Nightingale floor · Onigawara · Ranma · Shōji (see also washi) · Sōrin · Tamagaki · Tatami · Tokonoma · Tokyō · Tsumairi · ShibiGates and approaches Rooms Furnishings Outdoor objects Measurements Groups See also Buddhist temples in Japan Japanese Buddhist architecture Architectonic elements Mon (gates) Buildings Chinjusha · chōzuya/temizuya · -dō · main hall (kon-dō, hon-dō, butsuden) · kuri · kyōzō or kyō-dō · shoinTō or Buttō (pagodas) Styles Others A-un · kenSchools and objects of worship Major schools Zen schools Nanto rokushū Objects of worship Amida Nyōrai · Benzaiten · Dainichi Nyorai · Jizō · Kannon · Marishi-ten · Shaka Nyorai · Shitennō (Four Kings) · Twelve Heavenly Generals (Jūni Shinshō) · Yakushi NyoraiOther elements Implements kei (ritual gong) · mokugyōOthers bussokuseki · butsudan · Glossary of Japanese Buddhism · Japanese Buddhist pantheon · jingū-ji · miyadera · saisenbakoCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.