- Munger district
-
This article is about the district. For its eponymous headquarters, see Munger.
Munger district
मुंगेर जिला
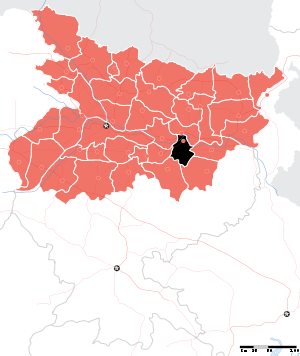
Location of Munger district in BiharState Bihar,  India
IndiaAdministrative division Munger Headquarters Munger Area 1,419.7 km2 (548.1 sq mi) Population 1,359,054 (2011) Population density 957 /km2 (2,480 /sq mi) Literacy 73.30 per cent[1] Sex ratio 879 Lok Sabha Constituencies Munger Assembly Seats Tarapur, Jamalpur and Munger Major highways NH-80 Average annual precipitation 1146 mm Official website Munger district is one of the thirty-eight districts of Bihar state in eastern India. Munger town is the administrative headquarters of this district. Munger district is a part of Munger Division. Its literacy rate of 73.3% is higher than the state literacy rate of 63.8% and lower than national rate of 74.04
Contents
Etymology
The district is named after its headquarters, Munger. There are several traditions regarding the etymology of Munger. According to one tradition, the present name of the town is derived from its ancient name Mudgagiri, which is mentioned in the Mahbharata as well as the Munger copperlate inscription of Devapala. According to another tradition, the name of the town is derived from either sage Mudgala or Maudgalyayana, a disciple of Buddha. However, General Cunnigham had strong suspicion that the original name of the town was connected with the Mundas, who are the earliest residents of this region and C.E.A. Oldham thinks it was probably derived from Munigriha (the abode of the Muni).
History
The territory occupied by the present day Munger district was a part of Anga mahajanapada. The Mahabharata says that it was ruled by Karna. Mudgagiri (Munger) was the capital of the Pala empire. Bengal Nawab Mir Kasim fought one of the last battles before the East India Company captured the eastern India. The Fort built by him has three gates and the Ganges on its fourth sides. Munger was known as Monghyr throughout British rule. In the early years of British rule Monghyr formed a part of Bhagalpur, and was not created a separate district till 1832.
Gaya has seen five districts partitioned off from its territory: Begusarai in 1976;[2] Khagaria in 1988;[2] and Jamui, Lakhisarai district, and Sheikhpura in 1999.[2]
The district is currently a part of the Red Corridor.[3]
Geography
Munger District is located in the southern part of Bihar and its headquarter is located on the southern bank of river Ganges. Munger district occupies an area of 1,419 square kilometres (548 sq mi),[4] comparatively equivalent to Russia's Urup Island.[5] It accounts for 3.3% of the area of Bihar . It lies between 240 22 N to 250 30 N latitude and 850 30 E to 870 3 E longitude.[6] Munger District was formed in 1832 out of Bhagalpur.
Bordered by river Ganges from north side. Lakhisarai and Begusarai districts(on the opposite banks of river Ganga) lies on the northwest and southwest side respectively. Jamui district on southern side, Bhagalpur and Banka districts on northeast and southeast sides respectively and Khagaria district on the northern side(across river Ganga).
Saharsa, Madhepura, Begusarai, Jamui, Sheikhpura, Khagaria and Lakhisarai districts were carved out of this district.
Munger district is so located in the southern Bihar and Munger town, its headquarters is located on the southern bank of the Ganges. The district lies between 24°20' and 25°30' north latitudes and between 85°37' and 87°30' east longitudes. The average height from the sea level is 30 to 65 m.
Rivers and lakes
The major rivers of this district are the Ganges, the Mohane, the Harohar and the Kiul.
Temple and village
Chandika temple is one of the famous temple in this city. Dalahatta Buzar Kumhartoli is as a small village, 80% people who staying here are kumhar by cast that make pot (Miiti ke bartan).Kalai is a village near Kharagpur having mostly bhrahmins and rajputs as its population.[7]
Climate
There are three distinct seasons in this zone, summer (March to May), monsoon (June to September) and winter (October to February). Average annual rainfall of this district is 1146 mm (average of 53 years).
Economy
In 2006 the Ministry of Panchayati Raj named Munger one of the country's 250 most backward districts (out of a total of 640).[8] It is one of the 36 districts in Bihar currently receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF).[8]
Divisions
The district is divided into three sub-divisions: Jamalpur, Kharagpur and Tarapur, which are further divided into nine development blocks:Kharagpur, Dharhara, mohanpur Munger, Jamalpur, Tarapur, Sangrampur, Bariarpur, Tetia Bambar and Asarganj.
Demographics
According to the 2011 census Munger district has a population of 1,359,054,[9] roughly equal to the nation of Swaziland[10] or the US state of Hawaii.[11] This gives it a ranking of 358th in India (out of a total of 640).[9] The district has a population density of 958 inhabitants per square kilometre (2,480 /sq mi) .[9] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 19.45 %.[9] Munger has a sex ratio of 879 females for every 1000 males,[9] and a literacy rate of 73.3 %.[9]
Languages
Languages used in the district include Angika, an Indo-Aryan language written in the Devanagari script and spoken by at least 725 000 people in the Angika Region.[12]
Flora and fauna
In 1976 Munger district became home to the Bhimbandh Wildlife Sanctuary, which has an area of 682 km2 (263.3 sq mi).[13]
References
- ^ "District-specific Literates and Literacy Rates, 2001". Registrar General, India, Ministry of Home Affairs. http://www.educationforallinindia.com/page157.html. Retrieved 2010-10-05.
- ^ a b c Law, Gwillim (2011-09-25). "Districts of India". Statoids. http://www.statoids.com/yin.html. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
- ^ "83 districts under the Security Related Expenditure Scheme". IntelliBriefs. 2009-12-11. http://intellibriefs.blogspot.com/2009/12/naxal-menace-83-districts-under.html. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- ^ Srivastava, Dayawanti et al. (ed.) (2010). "States and Union Territories: Bihar: Government". India 2010: A Reference Annual (54th ed.). New Delhi, India: Additional Director General, Publications Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India), Government of India. pp. 1118–1119. ISBN 978-81-230-1617-7.
- ^ "Island Directory Tables: Islands by Land Area". United Nations Environment Program. 1998-02-18. http://islands.unep.ch/Tiarea.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-11. "Urup 1,436km2"
- ^ http://munger.bih.nic.in/
- ^ http://ashishmunger.blogspot.com/
- ^ a b Ministry of Panchayati Raj (September 8, 2009). "A Note on the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme". National Institute of Rural Development. http://www.nird.org.in/brgf/doc/brgf_BackgroundNote.pdf. Retrieved September 27, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. http://www.census2011.co.in/district.php. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ^ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2119rank.html. Retrieved 2011-10-01. "Swaziland 1,370,424"
- ^ "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/apportionment-pop-text.php. Retrieved 2011-09-30. "Hawaii 1,360,301"
- ^ M. Paul Lewis, ed (2009). "Angika: A language of India". Ethnologue: Languages of the World (16th edition ed.). Dallas, Texas: SIL International. http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=anp. Retrieved 2011-09-28.
- ^ Indian Ministry of Forests and Environment. "Protected areas: Bihar". http://oldwww.wii.gov.in/envis/envis_pa_network/index.htm. Retrieved September 25, 2011.
External links

Begusarai district Khagaria district 
Lakhisarai district 
Bhagalpur district  Munger district
Munger district 

Jamui district Banka district Divisions and districts of Bihar, India Bhagalpur: Darbhanga: Kosi: Magadh: Munger: Patna: Purnia: Saran: Tirhut: Cities and towns in Munger Division Begusarai district Jamui district Khagaria district Munger district Lakhisarai district Sheikhpura district See also Munger Division topics • Villages in Munger divisionCities and towns
in other DivisionsMunger division topics General Districts Community development blocks Rivers Transport Lok Sabha constituencies Vidhan Sabha constituencies Begusarai Cheria-Baraiarpur • Bachwara • Teghra • Matihani • Sahebpur Kamal • Begusarai • Bakhri Khagaria Alauli • Khagaria • Beldaur • ParbattaFormer Vidhan Sabha constituencies Ballia • Barauni • ChauthamSee also Cities and towns in Munger Division • Villages in Munger division • People from Begusarai • Bihar topicsOther Divisions Bhagalpur • Darbhanga • Kosi • Magadh • Patna • Purnia • Saran • TirhutCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.