- tert-Butanol
-
tert-Butanol 
 2-Methylpropan-2-ol[1]Other namestert-Butyl alcohol[citation needed]
2-Methylpropan-2-ol[1]Other namestert-Butyl alcohol[citation needed]
Dimethylethanol[citation needed]
2-Methyl-2-propanol[citation needed]
1,1-Dimethylethanol[citation needed]Identifiers CAS number 75-65-0 
PubChem 6386 ChemSpider 6146 
UNII MD83SFE959 
EC number 200-889-7 UN number 1120 DrugBank DB03900 MeSH tert-Butyl+Alcohol ChEBI CHEBI:45895 
ChEMBL CHEMBL16502 
RTECS number EO1925000 Beilstein Reference 906698 Gmelin Reference 1833 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(C)(C)O
Properties Molecular formula C4H10O Molar mass 74.12 g mol−1 Exact mass 74.073164942 g mol−1 Appearance Colorless liquid Odor Camphorous Density 780.9 mg cm−3 Melting point 25-26 °C, 298-299 K, 77-79 °F
Boiling point 82-83 °C, 355-356 K, 179-181 °F
log P 0.584 Vapor pressure 4.1 kPa (at 20 °C) Refractive index (nD) 1.387 Thermochemistry Std enthalpy of
formation ΔfHo298−360.04–−358.36 kJ mol−1 Std enthalpy of
combustion ΔcHo298−2.64479–−2.64321 MJ mol−1 Standard molar
entropy So298189.5 J K−1 mol−1 Specific heat capacity, C 215.37 J K−1 mol−1 Hazards MSDS inchem.org GHS pictograms 

GHS signal word DANGER GHS hazard statements H225, H319, H332, H335 GHS precautionary statements P210, P261, P305+351+338 EU Index 603-005-00-1 EU classification  F
F  Xn
XnR-phrases R11, R20, R36/37 S-phrases (S2), S9, S16, S46 NFPA 704 Flash point 11 °C Autoignition
temperature480 °C Explosive limits 2.4–8.0% Related compounds Related butanols 2-Butanol
Related compounds 2-Methyl-2-butanol  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references tert-Butanol, or 2-methyl-2-propanol, is the simplest tertiary alcohol. It is one of the four isomers of butanol. tert-Butanol is a clear liquid (or a colorless solid, depending on the ambient temperature) with a camphor-like odor. It is very soluble in water and miscible with ethanol and diethyl ether. It is unique among the isomers of butanol because it tends to be a solid at room temperature, with a melting point slightly above 25 °C.
Contents
Preparation
tert-Butanol is derived commercially from isobutane as a co-product of propylene oxide production. It can also be produced by the catalytic hydration of isobutylene.
Applications
tert-Butanol is used as a solvent, as a denaturant for ethanol, as an ingredient in paint removers, as an octane booster for gasoline, as an oxygenate gasoline additive, and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemical commodities such as MTBE, ETBE, TBHP, other flavors and perfumes.
Chemistry
As a tertiary alcohol, tert-butanol is more stable to oxidation and less reactive than the other isomers of butanol.
When tert-butanol is deprotonated with a strong base, the product is an alkoxide anion. In this case, it is tert-butoxide. For example, the commonly used organic reagent potassium tert-butoxide is prepared by refluxing dry tert-butanol with potassium metal.[2]
- K + tBuOH → tBuO−K+ + 1/2 H2
The tert-butoxide species is itself useful as a strong, non-nucleophilic base in organic chemistry. It is able to abstract acidic protons from the substrate molecule readily, but its steric bulk inhibits the group from participating in nucleophilic substitution, such as in a Williamson ether synthesis or an SN2 reaction.
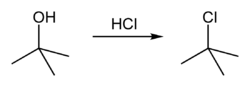
Conversion to alkyl halide
tert-Butanol reacts with hydrogen chloride to form tert-butyl chloride and water via an SN1 mechanism.
The overall reaction, therefore, is:
Because tert-butanol is a tertiary alcohol, the relative stability of the tert-butyl carbocation in the Step 2 allows the SN1 mechanism to be followed. Primary alcohols generally undergo an SN2 mechanism because the relative stability of a primary carbocation intermediate is very low. The tertiary carbocation in this case is stabilized through hyperconjugation where the neighboring C–H sigma bonds donate electrons into the empty p-orbital of the carbocation.
References
- ^ "tert-Butyl Alcohol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Cnter for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=6386&loc=ec_rcs. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
- ^ Johnson, William S.; Schneider, William P. (1950), "β-Carbethoxy-γ,γ-diphenylvinylacetic acid", Org. Synth. 30: 18, http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv4p0132; Coll. Vol. 4: 132
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0114
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards 0078
- IPCS Environmental Health Criteria 65: Butanols: four isomers
- IPCS Health and Safety Guide 7: tert-Butanol
Alcohols (0°) Primary alcohols (1°) Ethanol · 1-Propanol · Butanol/Isobutanol · 1-Pentanol · 1-Hexanol · 1-Heptanol
Fatty alcohol: Octanol (C8) · 1-Nonanol (C9) · 1-Decanol (C10) · Undecanol (C11) · Dodecanol (C12) · 1-Tetradecanol (C14) · Cetyl alcohol (C16) · Stearyl alcohol (C18) · Arachidyl alcohol (C20) · Docosanol (C22) · Tetracosanol (C24) · Hexacosanol (C26) · Octanosol (C28) · Triacontanol (C30)
PolicosanolSecondary alcohols (2°) Isopropyl alcohol · 2-Butanol · 2-Hexanol · Cyclohexanol
Tertiary alcohols (3°) tert-Butanol · 2-Methyl-2-butanol
biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iCategories:- Alcohols
- Alcohol solvents
- Oxygenates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.