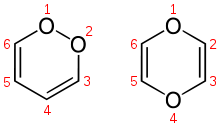
- 1,4-Dioxin
-
For the general class of dioxin compounds which are environmental pollutants, see polychlorinated dibenzodioxins.Not to be confused with dioxane or digoxin.
1,4-Dioxin 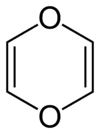
 1,4-DioxineOther namesp-dioxin, dioxin
1,4-DioxineOther namesp-dioxin, dioxinIdentifiers CAS number 290-67-5 ChemSpider 71301 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O\1/C=C\O/C=C/1
Properties Molecular formula C4H4O2 Molar mass 84.07 g/mol Appearance Colorless liquid Boiling point 75 °C, 348 K, 167 °F
Hazards Main hazards highly flammable Related compounds Related compounds 1,2-dioxin, dibenzodioxin  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 1,4-Dioxin (also referred as dioxin or p-dioxin) is a heterocyclic, organic, antiaromatic compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2.
There is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin, 1,2-dioxin (or o-dioxin). 1,2-Dioxin is very unstable due to its peroxide-like characteristics.
The term “dioxin” is most commonly used for a family of derivatives of dioxin, known as polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs).
Contents
Preparation
1,4-Dioxin can be prepared by cycloaddition, namely by the Diels–Alder reaction of furan and maleic anhydride. The adduct formed has a carbon-carbon double bond, which is converted to an epoxide. The epoxide then undergoes a retro-Diels–Alder reaction, forming 1,4-dioxin and regenerating maleic anhydride.[1]
Derivatives
 Figure 1: The skeletal formula and substituent numbering scheme of dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, the parent compound of PCDDs
Figure 1: The skeletal formula and substituent numbering scheme of dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, the parent compound of PCDDs
The word “dioxin” can refer in a general way to compounds which have a dioxin core skeletal structure with substituent molecular groups attached to it. For example, dibenzo-1,4-dioxin is a compound whose structure consists of two benzo- groups fused onto a 1,4-dioxin ring.
Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins
Main article: polychlorinated dibenzodioxinsBecause of their extreme importance as environmental pollutants, current scientific literature uses the name dioxins commonly for simplification to denote the chlorinated derivatives of dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, more precisely the polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs), among which 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (TCDD), a tetrachlorinated derivative, is the best known. The polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, which can also be classified in the family of halogenated organic compounds, have been shown to bioaccumulate in humans and wildlife due to their lipophilic properties, and are known teratogens, mutagens, and carcinogens.
PCDDs are formed through combustion, chlorine bleaching and manufacturing processes.[2] The combination of heat and chlorine creates dioxin.[2] Since chlorine is often a part of the Earth's environment, natural ecological activity such as volcanic activity and forest fires can lead to the formation of PCDDs.[2] Nevertheless, PCDDs are mostly created by human activity.[2]
Famous PCDD exposure cases include Agent Orange produced by Monsanto sprayed over vegetation during the Vietnam war, the Seveso disaster, and the poisoning of Viktor Yushchenko.
Polychlorinated dibenzofurans are a related class compounds to PCDDs which are often included within the general term “dioxins”.
References
- ^ Aitken, R. Alan; Cadogan, J. I. G. & Gosneya, Ian (1994). "Effect of ring strain on the formation and pyrolysis of some Diels–Alder adducts of 2-sulfolene (2,3-dihydrothiophene 1,1-dioxide) and maleic anhydride with 1,3-dienes and products derived therefrom". J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 (8): 927–931. doi:10.1039/p19940000927.
- ^ a b c d Dioxin from State of Maine's Department of Environmental Protection
Categories:- Dioxins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.