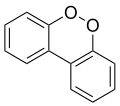
- Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin
-
Dibenzo-p-dioxin 
 Dibenzo-1,4-dioxinOther namesDibenzodioxin,
Dibenzo-1,4-dioxinOther namesDibenzodioxin,
Dibenzo-p-dioxin,
OxanthreneIdentifiers CAS number 262-12-4 
ChemSpider 8861 
KEGG C07732 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O1c3c(Oc2c1cccc2)cccc3
Properties Molecular formula C12H8O2 Molar mass 184.19 g mol−1 Appearance White crystals Melting point 122 °C, 395 K, 252 °F
Boiling point 283.5 °C, 557 K, 542 °F
Related compounds Related compounds dioxin
1,4-dioxin
polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dibenzo-p-dioxin (dibenzo-para-dioxin) or dibenzo-1,4-dioxin is an organic heterocyclic compound in which two benzene rings are connected by a 1,4-dioxin ring. Its molecular formula is C12H8O2. The two oxygen atoms occupy opposite (para) positions in a six-membered dioxin ring.
The isomeric compound dibenzo-o-dioxin or dibenzo-1,2-dioxin has two adjacent oxygen atoms (ortho). As no detailed information is available on the dibenzo-ortho-dioxin isomer, it is expected to be highly unstable, with peroxide-like characteristics.
The general name dibenzodioxin usually refers to dibenzo-p-dioxin.
Dibenzodioxin forms the scaffold for the class of chemicals known collectively as dioxins, which include the potent toxins polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs) such as 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin.
See also
- Thianthrene, the sulfur analog of dibenzodioxin
- 1,2-dioxane
References
Categories:- Dibenzodioxins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.