- Zethrene
-
Zethrene 
 dibenzo[de,mn]tetracene
dibenzo[de,mn]tetraceneIdentifiers CAS number 214-63-1 ChemSpider 11562880 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1ccc3c6c1cccc6\C=C/2\c4cccc5cccc(\C=C\23)c45
- InChI=InChI=1S/C24H14/c1-5-15-7-3-11-19-22-14-18-10-2-6-16-8-4-12-20(24(16)18)21(22)13-17(9-1)23(15)19/h1-14H
Properties Molecular formula C24H14 Molar mass 302.37 g mol−1 Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Dibenzo[de,mn]naphthacene or zethrene is an aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of two phenalene units fused together. According to Clar's rule the two exterior naphtalene units are truly aromatic and the two central double bonds are not aromatic at all. For this reason the compound is of some interest to academic research. Zethrene is air and light sensitive (complete decomposition under a sunlight lamp within 12 hours) with a deep-red color. The melting point is 262 °C.
Synthesis
The compound was first synthesised by Erich Clar in 1955 [1] from acenaphthene in one method and from chrysene in another. Mitchell & Sondheimer prepared the compound from a benzannulated [10]annulene.[2][3]
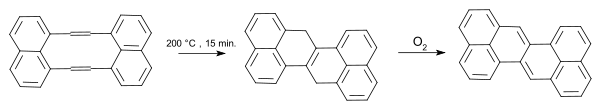
Zethrene synthesis 1968 Sondheimer A sulfur extrusion method was reported by Kemp, Storie & Tulloch.[4] Wu et al.[5] reported the synthesis of the compound in a coupling reaction / dimerization with in-situ desilylization.
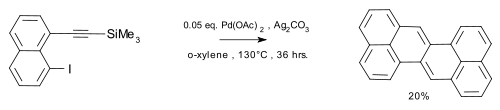
Zethrene synthesis Wu 2010 Derivatives are also known.[6][7]
Structure
X-ray crystallography indicates that zethrene is a planar molecule.[5] The bond lengths in the central part of the molecule are consistent with distinct single and double bonds rather than aromatic components.
References
- ^ Clar, Erich; Lang, Karl Friedrich; Schulz-Kiesow, Hans (1955). "Aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffe, LXX. Mitteil.1): Zethren (1.12; 6.7-Dibenztetracen)". Chemische Berichte 88 (10): 1520. doi:10.1002/cber.19550881008.
- ^ Mitchell, Reginald Harry; Sondheimer, Franz (1968). "A dinaphth[10]annulene". Journal of the American Chemical Society 90 (2): 530. doi:10.1021/ja01004a080.
- ^ Mitchell, R.H.; Sondheimer, F. (1970). "The attempted synthesis of a dinaphth-1,6-bisdehydro[10]annulene". Tetrahedron 26 (9): 2141. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)92792-9.
- ^ Kemp, William; Storie, Iain T.; Tulloch, Charles D. (1980). "Synthesis of potentially basic hydrocarbons by sulphur extrusion and/or bis-Wittig reactions. Two syntheses of benz[5,6]indeno[2,1-a]phenalene and a new synthesis of dibenzo[de,mn]naphthacene (zethrene)". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1: 2812. doi:10.1039/P19800002812.
- ^ a b Wu, Tsun-Cheng; Chen, Chia-Hua; Hibi, Daijiro; Shimizu, Akihiro; Tobe, Yoshito; Wu, Yao-Ting (2010). "Synthesis, Structure, and Photophysical Properties of Dibenzo[de,mn]naphthacenes". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 49 (39): 7059. doi:10.1002/anie.201001929.
- ^ Umeda, Rui; Hibi, Daijiro; Miki, Koji; Tobe, Yoshito (2009). "Tetradehydrodinaphtho[10]annulene: A Hitherto Unknown Dehydroannulene and a Viable Precursor to Stable Zethrene Derivatives". Organic Letters 11 (18): 4104. doi:10.1021/ol9015942.
- ^ Sun, Zhe; Huang, Kuo-Wei; Wu, Jishan (2010). "Soluble and Stable Zethrenebis(dicarboximide) and Its Quinone". Organic Letters 12 (20): 100923111447081. doi:10.1021/ol102088j.
2 rings 3 rings 4 rings 5 rings 6+ rings Anthanthrene · Benzo[ghi]perylene · Corannulene · Coronene · Dicoronylene · Diindenoperylene · Helicene · Heptacene · Hexacene · Kekulene · Ovalene · ZethreneCategories:- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.