- Government of Delhi
-
Government of Delhi 
State EmblemSeat of Government Delhi Executive Governor Tejendra Khanna Chief Minister Sheila Dixit Legislature Speaker Yoganand Shastri Deputy Speaker Amrish Singh Gautam Members in Assembly 70 Judiciary High Court Delhi High Court Chief Justice K. S. Hegde delhigovt.nic.in The Government of Delhi is the supreme governing authority of the Indian national capital territory of Delhi and its 9 districts. It consists of an executive, led by the Lieutenant Governor of Delhi, a judiciary and a legislative. The present Legislative Assembly of Delhi is unicameral, consisting of 70 Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLA).
Contents
Overview
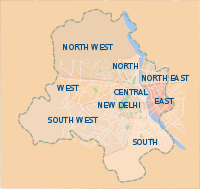 The nine districts of Delhi.
The nine districts of Delhi.
The Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) handles civic administration for the city as part of the Panchayati Raj Act. New Delhi, an urban area in Delhi, is the seat of both the State Government of Delhi and the Government of India. The National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT) has three local municipal corporations namely, Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD), New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC) and Delhi Cantonment Board.
The head of state of Delhi is the Lieutenant Governor of Delhi, appointed by the President of India on the advice of the Central government and the post is largely ceremonial, as the Chief Minister of Delhi is the head of government and is vested with most of the executive powers. The present chief Minister is Sheila Dikshit, who is currently serving her third consecutive term since 1998.
The Delhi High Court has jurisdiction over Delhi, which also has two lower courts: the Small Causes Court for civil cases, and the Sessions Court for criminal cases. The Delhi Police, headed by the Police Commissioner, is one of the largest metropolitan police forces in the world.[1] The headquarters of Delhi Police are located at ITO, a Delhi landmark that connects East Delhi (popularly known as Yamuna paar) to the rest of the city.
History
Legislative Assembly of Delhi was first constituted on 17 March 1952 under the Government of Part C States Act, 1951, but it was abolished on 1 October 1956. It was legislative assembly was re-established in 1993, after the Constitution (Sixty-ninth Amendment) Act, 1991 came into force, followed by the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi Act, 1991 the Sixty-ninth Amendment to the Constitution of India, declared the Union Territory of Delhi to be formally known as National Capital Territory of Delhi.[2]
The first Chief minister of Delhi was Ch. Braham Prakash (INC) and the first women CM was Sushma Swaraj of BJP. Comrade Guru Kishan (CPI) had the rare distinction of representing his constituency in MCD (DMC initially) for most years continuously by an individual and Ch. Prem Singh (INC) has won the maximum elections for different civic bodies in Delhi.
References
- ^ "History of Delhi Police". Delhi Police Headquarters, New Delhi, India. http://www.delhipolice.nic.in/home/history1.htm.
- ^ THE CONSTITUTION (Sixty-ninth Amendment) Act, 1991
- Vajpeyi, S. C.; S. P. Verma (1998). Landmarks in Delhi administration (post-independence era), 1947-97. Gyan Books. ISBN 8121205689. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=NTHb_NpdhWsC&pg=PA166&dq=Delhi+administration&hl=en&ei=rpBITKC-KcGecaDs9eIM&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDAQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false.
External links
Government of India State governments Andhra Pradesh · Arunachal Pradesh · Assam · Bihar · Chhattisgarh · Goa · Gujarat · Haryana · Himachal Pradesh · Jammu and Kashmir · Jharkhand · Karnataka · Kerala · Madhya Pradesh · Maharashtra · Manipur · Meghalaya · Mizoram · Nagaland · Orissa · Punjab · Rajasthan · Sikkim · Tamil Nadu · Tripura · Uttar Pradesh · Uttarakhand · West BengalNCT DelhiTerritories Andaman and Nicobar Islands · Chandigarh · Dadra and Nagar Haveli · Daman and Diu · Lakshadweep · PuducherryCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
