- Cryogenic nitrogen plant
-
Nitrogen, as an element of great technical importance, can be produced in a cryogenic nitrogen plant with a purity of more than 99.9999%.
Air inside a distillation column is separated at cryogenic temperatures (about 100K/-173°C) to produce high purity nitrogen with 1ppm of impurities. The process is based on the air separation, which was invented by Dr. Carl von Linde in 1895.
Contents
Purpose
The main purpose of a cryogenic nitrogen plant is to provide a customer with high purity gaseous nitrogen (GAN). In addition liquid nitrogen (LIN) is produced simultaneously and is typically 10% of the gas production. High purity liquid nitrogen produced by cryogenic plants is stored in a local tank and used as a strategic reserve. This liquid can be vaporised to cover peaks in demand or for use when the nitrogen plant is offline. Typical cryogenic nitrogen plants range from 250 Nm3/hour to very large range plants such as the Cantarell Field plant in Mexico with a daily capacity of 63.000 tonnes of nitrogen a day.[1]
Plant Modules
A cryogenic nitrogen plant comprises:
Warm End (W/E) Container
- Compressor
- Air receiver
- Chiller (Heat exchanger)
- Pre-filter
- Air purification unit (APU)
Coldbox
- Main heat exchanger
- Distillation Column
- Condenser
- Expansion brake turbine
Storage and Backup System
- Liquid nitrogen tank
- Vapouriser
How the plant works
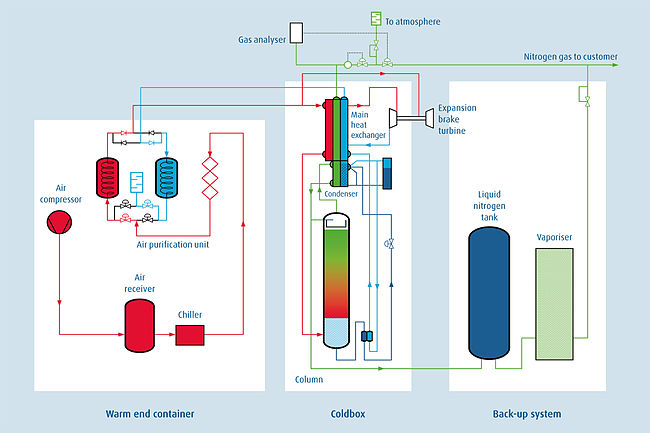 Flowsheet GAN Plant Linde Cryoplants Ltd.
Flowsheet GAN Plant Linde Cryoplants Ltd.
Warm end process
Atmospheric air is roughly filtered and pressurised by a compressor, which provides the product pressure to deliver to the customer. The amount of air sucked in depends on the customer’s nitrogen demand.
The Air Receiver collects condensate and minimises pressure drop. The dry and compressed air leaves the air to refrigerant heat exchanger at about 10°C.
To clean the process air further, there are different stages of filtration. First of all, more condensate is removed, than a Coalescing filter acts as a gravity filter and finally an adsorber filled with activated carbon removes some hydrocarbons.
The last unit process in the warm end container is the thermal swing adsorber (TSA). The Air purification unit cleans the compressed process air by removing any residual water vapour, carbon dioxide and hydrocarbons. It comprises two vessels, valves and exhaust to allow the changeover of vessels. While one of the TSA beds is on stream the second one is regenerated by the oxygen rich waste flow, which is vented through a silencer into the ambient environment.
Coldbox process
After leaving the air purification unit, the process air enters the main heat exchanger, where it is rapidly cooled down to -165°C. All residual impurities (e.g. CO2) freeze out, and the process air enters at the bottom of the distillation column partially liquefied.
The distillation column comprises a liquid distributor at the top, several meters of structured packing with liquid redistributors and a bottom reservoir for the liquid flowing down the column. Pure nitrogen is separated on top of the column and oxygen enriched liquid remains at the bottom.
The oxygen enriched liquid passes to the condenser by means of a Joule-Thomson expansion valve, which flushes off some of the liquid as vapour and cools the remaining liquid. This sub cooled liquid condenses some of the pure nitrogen gas stream coming off the top of the column. Part of the condensed nitrogen is passed into the distillation column to maintain the purity, the remaining liquid is stored in a local storage tank as a strategic reserve. Nitrogen that is not condensed passes through the main heat exchanger and becomes the product delivered to the costumer.
The waste gas, which is subsequently generated as the sub- cooled oxygen enriched liquid is vaporised in the condenser, returns to the APU where it is used to regenerate the desiccant. Refrigeration for the process is provided by air brake expansion turbines located at the base of the cold box. A stream of high-pressure gas from the heat exchangers (-110°C) is expanded to low pressure and cooled in the turbine. The cooled air (-160°C) returns to the waste stream of the heat exchangers to provide refrigeration.
The energy that is removed by the turbine appears as heat in the turbine cooling system.
Back up process
Liquid Nitrogen produced from the cold box transfers into the liquid storage tank. An ambient air vaporiser is used to vaporise stored liquid during peak demand. A pressure control panel senses the demand for gaseous nitrogen and regulates the gas flow into the end-users pipeline to maintain a present line-pressure.
Applications for high purity nitrogen production
- Ammonia production for the fertilizer industry
- Float glass manufacture
- Petrochemical
- Inerting headspace in Tanks
- Blanketing
- Amine gas treatment
- Bearing seal gas
- Polyester manufacture
- Semiconductor manufacture
- Photovoltaic manufacture
References
External links
- Linde CryoPlants Ltd ,World leading manufacturer of midrange cryogenic nitrogen plants
- Linde Group
Categories:- Chemical processes
- Thermodynamic processes
- Gases
- Industry
- Industrial processes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

