- Carbonyl reduction
-
Carbonyl reduction in organic chemistry is the organic reduction of any carbonyl group containing compound by a reducing agent. Typical carbonyl compounds are ketones , aldehydes, carboxylic acids and esters. A carbonyl group can be reduced to the alcohol or the oxygen atom can be removed altogether, a process called deoxygenation. Many reducing agents are metal hydrides based on boron and aluminum. A second important method is catalytic hydrogenation. [1] [2].
Contents
Metal hydride mechanism
The reaction mechanism for metal hydride reduction is based on activation of the carbonyl group by the metal followed by nucleophilic addition of hydride. Another general system is catalytic hydrogenation by metal. LiAlH4 is more reactive than NaAlH4 because the smaller lithium cation is a better Lewis acid. A crown ether reduces reactivity. Alkoxide substitution in metal hydrides increases solubility and selectivity. An example is Red-Al.
Aldehyde and ketone reduction
The reaction product of the reduction of an aldehyde is a primary alcohol and that of a ketone a secondary alcohol. Reagents are lithium aluminium hydride [3] [4] [5], diisobutylaluminium hydride, sodium borohydride, L-selectride, diborane, diazene and aluminum hydride. Sodium borohydride tolerates more functional groups (nitro group, nitrile, ester) than LiAlH4 and can also be used with water or ethanol as a solvent (LiAlH4 reacts with protic solvents). Sodium cyanoborohydride, 9-BBN-pyridine and tributyltin hydride are selective for aldehydes. A method for selective ketone reduction in presence of an aldehyde is NaBH4 / cerium chloride.
In hydrogenation platinum and ruthenium are preferred catalysts. Specific methods are the Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction (aluminumisopropylate/isopropanol), the Bouveault–Blanc reduction (sodium metal/ethanol) and the Cannizzaro reaction (KOH induced aldehyde disproportionation)
Carboxylic acid reduction
Typical reagents for the reduction of carboxylic acids or carboxylate salts to alcohols are lithium aluminium hydride , diborane, DIBAL and aluminum hydride. Catalytic hydrogenation and NaBH4 are ineffective.
Ester reduction
Esters (R(CO)OR') can be reduced to alcohols RCH2OH and R'OH by lithium aluminium hydride [6] [7] and aluminum hydride. Diisobutylaluminium hydride and lithium tri-t-butoxyaluminum hydride are selective for the formation of the aldehyde. Catalytic hydrogenation over copper chromite is reported.
1,4-reduction
In 1,4-reduction (also called conjugate reduction) the reaction substrate is an unsaturated carbonyl compound, an enone or enal. The 1,2-reduction product (an allyl alcohol) competes with 1,4-reduction to the saturated ketone or aldehyde. In 1,4-reduction the first step is conjugate addition of the hydride to the enolate ion followed by acidic workup forming the ketone.
1,2-reduction is found with DIBAL and 9-BBN and alane. 1,4-reduction can be accomplished with catalytic hydrogenation and by alkylmetal hydrides.
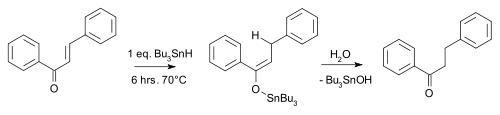
An example is the reduction of chalcone by tributyltin hydride [8]:
Conjugate reduction chalcone An asymmetric version of this reaction has also been developed [9].
Asymmetric synthesis
Main article: Asymmetric catalytic reductionMain article: Enantioselective reduction of ketonesWell known carbonyl reductions in asymmetric synthesis are the Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation (beta-ketoester reduction /Ru/BINAP) and the CBS reduction (BH3, proline derived chiral catalyst).
References
- ^ Advanced organic chemistry: Structure and mechanisms Francis A. Carey, Richard J. Sundberg 2nd Ed.
- ^ March, Jerry (1985), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (3rd ed.), New York: Wiley, ISBN 0-471-85472-7
- ^ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 7, p.129 (1990); Vol. 60, p.25 (1981). Link
- ^ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p.887 (1988); Vol. 58, p.12 (1978). Link
- ^ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p.769 (1988); Vol. 56, p.101 (1977). Link
- ^ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p.781 (1988); Vol. 53, p.70 (1973). Link
- ^ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 4, p.834 (1963); Vol. 33, p.82 (1953). link
- ^ Leusink, A.J.; Noltes, J.G. (1966). "Reaction of organotin hydrides with α,β-unsaturated ketones". Tetrahedron Letters 7 (20): 2221. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)72405-1.
- ^ Moritani, Yasunori; Appella, Daniel H.; Jurkauskas, Valdas; Buchwald, Stephen L. (2000). "Synthesis of β-Alkyl Cyclopentanones in High Enantiomeric Excess via Copper-Catalyzed Asymmetric Conjugate Reduction". Journal of the American Chemical Society 122 (28): 6797. doi:10.1021/ja0009525.
Categories:- Organic redox reactions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.