- Common External Power Supply
-
In 2009 several government, consumer and industry initiatives resulted in the European Union's definition of a common External Power Supply (EPS) for use with data-enabled mobile phones sold in the EU. An external power supply is the AC power adapter that converts household AC voltages to the much lower DC voltages needed to charge a mobile phone's internal battery. The primary goal for creation of a standard / common external power supply is to eliminate waste by reducing the total number of power adapters manufactured and sold with mobile phones. The hope is that by creating a common external power supply specification (and then getting all mobile phone manufacturers to design their phones to be compatible with the specified power supply), EU consumers will be able to re-use the same external power supply with different phones from different manufacturers. Mobile phone manufacturers will then not feel compelled to provide a new external power supply with every phone sold.
Contents
History
USB battery charging specification
As USB communication ports became widely available on computers/laptops, some manufacturers of small electronic devices (including mobile phone manufacturers) began to design their battery-powered products to support being charged from a computer's USB port - or from a dedicated AC power adapter with an integrated USB port. The USB Implementers Forum, recognizing this trend, updated the USB standard to better accommodate this popular battery-charging application of USB ports. The resulting "USB Battery Charging" specification was officially released in March, 2007.[1] The USB battery charging specification defines, "...limits as well as detection, control and reporting mechanisms to permit devices to draw current in excess of the USB 2.0 specification for charging and/or powering up..."[2]
EU common External Power Supply (EPS)
In June 2009, many of the world's largest mobile phone manufacturers signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), agreeing to make most new data-enabled mobile phones marketed in the European Union compatible with a to-be-specified common External Power Supply (EPS). All signatories agreed to develop a common specification for the EPS "to allow for full compatibility and safety of chargers and mobile phones."[3] As of 2011, 14 mobile phone manufacturers and technology providers have signed the MoU — the original 10 signatories, Apple, LG, Motorola, NEC, Nokia, Qualcomm, RIM, Samsung, Sony Ericsson, and Texas Instruments as well as Atmel, Emblaze Mobile, Huawei Technologies and TCT Mobile (Alcatel).[4]
In order to develop and formalize the needed technical standards, the European Commission issued a standardisation mandate to CEN, CENELEC and ETSI on a common Charging Capability for Mobile Telephones. In response to this mandate, CENELEC created a task force to develop the interoperability specifications of the common External Power Supply. The resulting technical specifications were published in December 2010 as EN 62684:2010, “Interoperability specifications of common external power supply (EPS) for use with data-enabled mobile telephones."[5] The common EPS specification references USB electro-mechanical interface standards and, in March 2011, the USB Implementers Forum agreed to allow CENELEC "...to make reference to USB technology in its European Standard EN62684:2010 and...to grant download access to USB technical specifications free of charge and at any time to manufacturers implementing this European Standard."[6]
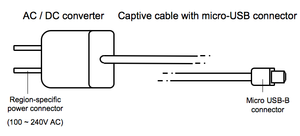
Cabling and adapters
Unlike some other proposed mobile phone power supply standards[7] the EU's common External Power Supply (EPS) specification allows for chargers with either (a) a USB-A socket and detachable (USB-A connector to Micro USB-B connector) cable or (b) no socket and a 'captive' cable terminated with a Micro USB-B connector.[8] The MoU which defines the common External Power Supply (EPS) as well as the related EU standardisation mandate both allow for the use of the common External Power Supply also with phones not equipped with a Micro USB receptacle. "...[MoU] 4.2.1...if a manufacturer makes available an Adaptor from the Micro-USB connector of a Common EPS to a specific non-Micro-USB socket in the Mobile Phone, it shall constitute compliance to this article" and, "...An Adaptor can also be a detachable cable."[9][10]
Reception
The common EPS initiative was generally well received although at least one European consumer group bemoaned the voluntary nature and narrow scope of the initiative (hand-held data-enabled mobile phones only) and the fact that the EU's EPS specification does not set aggressive energy efficiency (no-load consumption) requirements.[11]
Similar regional and global industry initiatives
Other similar power supply / charging solutions standards have been implemented in other regions (e.g. Korea and China). An industry-wide (GSMA / OMTP) proposal also exists for a common, energy efficient mobile phone charging solution although it has not yet been adopted by as many phone manufacturers as has the EU standard.
Charger and Interface standard in South Korea
In March 2001, the Korean Telecommunications Technology Association (TTA) released the "Standard on I/O Connection Interface of Digital Cellular Phone."[12] The standard describes the electromechanical interface specifications for cellular phone charging, wired data communication, analog audio, etc. and was released together with related test and certification specifications.[13][14] The main feature of the standard is the specification of a 24 pin connector / socket for mobile phones to handle connections for power input (battery charging) and output, data communication (USB and other digital signals), analog audio inputs and outputs (for hands-free microphone, earphone) and other signals. The 2007 revision of the standard[15] specified a smaller 20 pin connector to succeed the 24 pin connector and added analog (composite) video output support, among other changes. Chargers with the new 20 pin connectors started appearing in 2008 and phone manufacturers were urged to include 24 to 20 pin adapters with new phones sold in Korea to enable the charging of new phones with the older 24 pin chargers.[16]
Charger and Interface standard in the People's Republic of China
In December 2006, the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MII) released a new CCSA (China Communications Standards Association) standard, "Technical Requirements and Test Method of Charger and Interface for Mobile Telecommunication Terminal Equipment."[17] The standard describes the electromechanical requirements for a common mobile device battery charger equipped with a USB-A socket providing 5V DC power. All new mobile phones requesting network access approval in China from June 2007 are required to support charging from the new common chargers. The original 2006 regulation is flexible regarding the interface on the mobile phone itself, allowing for the use of adapter cables if the mobile device is not equipped with a standard USB connector.[18] Among other things, the 2009 update adds references to USB On-The-Go (OTG) support and the use of USB Micro B, USB Micro AB, USB Mini B, USB Mini 10 pin and cylindrical ("barrel") type connectors on the terminal (phone) for charging.[19]
GSMA / OMTP Universal Charging Solution (UCS) / Common Charging Solution (CCS)
In February 2009, the GSM Association (GSMA), together with 6 mobile phone manufacturers and technology providers and 11 mobile service providers, announced their commitment to implementing a cross-industry standard for a common / universal charging solution for new mobile phones and chargers. The aim of the GSMA initiative is, "...to ensure that the mobile industry adopts a common format for mobile phone charger connections and energy-efficient chargers...". Universal Charging Solution (UCS) chargers are to use Micro-USB as the common universal charging interface and have a 4-star or higher efficiency rating (standby energy use ≤0.15W).[20]
OMTP (the Open Mobile Terminal Platform industry forum) specified the requirements of the GSMA's Universal Charging Solution and published these requirements under the title "Common Charging and Local Data Connectivity" in 2009. This document specifies the three components of a Common Charging Solution (CCS): a Charging and Local Data Connector (CLD) on the "terminal" (e.g. mobile phone) consisting of a USB Micro-B or USB Micro-AB socket; a Common Power Supply (CPS) with a USB-A socket; and a detachable USB-A to USB Micro-B cable to connect the power supply with the mobile phone.[21] As of early 2011, an additional 10 service providers and one additional mobile phone manufacturer have joined the agreement.[22]
In April, 2009, the industry trade group CTIA announced its support of the GSMA's Universal Charging Solution.[23] The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) announced in October 2009 that it had also embraced the Universal Charging Solution standard - based on input from the GSMA - as its "energy-efficient one-charger-fits-all new mobile phone solution."[24]
References and notes
- ^ (USB Battery Charging specification released in March, 2007 (version 1.0) with updates in 2009 (version 1.1) and 2010 (version 1.2))
- ^ "USB-IF Enhances Battery Charging Capabilities with New Spec." (PDF). 2007-04-17. http://www.usb.org/press/pressroom/2007_04_17_usbif3.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-21.
- ^ "EUROPA - Press Releases - Harmonisation of a charging capability of common charger for mobile phones". Europa.eu. 2009-06-29. http://europa.eu/rapid/pressReleasesAction.do?reference=MEMO/09/301. Retrieved 2010-08-26.
- ^ "Cellphone charger harmonization". ec.europa.eu. http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/sectors/rtte/chargers/index_en.htm. Retrieved 2011-01-21.
- ^ "New standard for common mobile chargers". cenelec.eu. 2011-01-11. http://www.cenelec.eu/pls/apex/f?p=WEB:NEWSBODY:3695278126835242::NO::P300_NEWS_ID:21. Retrieved 2011-01-21.
- ^ "Agreement reached on the Micro-USB connector and the standard for the common mobile charger..." (PDF). 2011-03-01. http://www.usb.org/press/USB-IF_Press_Releases/CENELEC_USB-IF.PDF. Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ (e.g. the OMTP Common Charging Solution's CPS specification which mandates a charger with a USB-A socket and a (mandatory) detachable cable. "Captive" cables are not allowed)
- ^ "Annex II, Technical Annex to MoU regarding the Harmonisation of a Charging Capability for Mobile Phones" (PDF). 2010-01-12. http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/sectors/rtte/files/chargers/chargers_annex_ii_to_mou_january_12_2010_en.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-26.
- ^ "MoU regarding Harmonisation of a Charging Capability for Mobile Phones" (PDF). 2009-06-05. http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/sectors/rtte/files/chargers/chargers_mou_en.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-06.
- ^ "Standardisation mandate to CEN, CENELEC and ETSI on a common Charging Capability for Mobile Telephones" (PDF). 2009-10-01. http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/sectors/rtte/files/chargers/m455_chargers_en.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-21.
- ^ "The universal charger: not quite universal yet" (PDF). 2010-12-29. http://www.anec.org/attachments/ANEC-PR-2010-PRL-019.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-26.
- ^ "Standard on I/O Connection Interface of Digital Cellular Phone" TTAS.KO-06.0028 released in March 2001. Later updated in 2002 (/R2), and in 2007 (/R4))
- ^ Related test and certification standards published (TTAS.KO-06.0029 and TTAS.KO-06.0030).
- ^ "Standard on Integrated I/O Connection Interface for Mobile Phone". Korean Telecommunications Technology Association (TTA). 2001-11-08. http://www.tta.or.kr/data/ttas_view.jsp?pk_num=TTAS.KO-06.0028/R4&nowSu=1. Retrieved 2011-03-30.
- ^ (2007 revision = TTAS.KO-06.0028/R3)
- ^ "TTA certifies first 20-pin battery charger for mobiles". Telecompaper.com. 2008-07-25. http://www.telecompaper.com/news/tta-certifies-first-20pin-battery-charger-for-mobiles. Retrieved 2011-03-30.
- ^ "Technical Requirements and Test Method of Charger and Interface for Mobile Telecommunication Terminal Equipment" (CCSA YD/T 1591-2006, later updated to YD/T 1591-2009)
- ^ "How to conform to China's new mobile phone interface standards". EETimes.com. 2007-10-22. http://www.eetimes.com/design/communications-design/4016269/How-to-conform-to-China-s-new-mobile-phone-interface-standards?pageNumber=0. Retrieved 2011-02-21.
- ^ "YD 1591-2009 移动通信终端电源适配器及充电/数据接口技术要求和测试方法 ((introduction to) Mobile Communication Terminal Adapter and Charging / Data interface Technical Requirements and Test Methods)". China Communications Standards Association (CCSA.org.cn). 2010-08-04. http://www.ccsa.org.cn/article_new/show_article.php?categories_id=ccc49e22-587d-8397-4ff9-460c5ed9bf46&article_id=bzjs_2842bccf-7e49-0a74-8a92-4c58d44ef1d4. Retrieved 2011-04-05.
- ^ "GSM World agreement on Mobile phone Standard Charger". http://www.gsmworld.com/newsroom/press-releases/2009/2548.htm.
- ^ OMTP: Common Charging and Local Data Connectivity V1.0, 2009-02-11 (Final revision V1.1 published in 2010)
- ^ "Partners" (html). 2011. http://gsmworld.com/our-work/mobile_planet/green_power_for_mobile/partners.htm. Retrieved 2011-04-10.
- ^ "Press Release: CTIA–The Wireless Association® Announces One Universal Charger Solution to Celebrate Earth Day". ctia.org. 2009-04-22. http://www.ctia.org/media/press/body.cfm/prid/1817. Retrieved 2011-01-21.
- ^ "Press Release: Universal phone charger standard approved — One-size-fits-all solution will dramatically cut waste and GHG emissions". Itu.int. 2009-10-22. http://www.itu.int/newsroom/press_releases/2009/49.html. Retrieved 2009-11-04.
External links
- Battery Charging v1.2 Spec. and Adopters Agreement USB Implementers Forum, 2010-12-07.
- Universal Charging Solution Explained, GSMA UCS Project Team, 2009
- OMTP: Common Charging and Local Data Connectivity V1.1 (Final) OMTP Local Connectivity Recommendations V1.1, OMTP Limited, 2010-06-08.
- MoU regarding Harmonisation of a Charging Capability for Mobile Phones, 2009 June 5
- M/455 EN - Standardisation mandate to CEN, CENELEC and ETSI on a common Charging Capability for Mobile Telephones, 2009 October 1
- EN 62684:2010 "Interoperability specifications of common external power supply (EPS) for use with data-enabled mobile telephones"
- EN 301489-34 V1.1.1 (Final draft 2010-05) "ElectroMagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment and services - Part 34: Specific conditions for External Power Supply (EPS) for mobile phones"
- One Charger For All.eu, European Commission Enterprise and Industry Directorate - General
- CCSA YD/T 1591-2006, "Technical Requirement and Test Method of Charger and Interface for Mobile Telecommunication Terminal Equipment", Published by the Ministry of Information and Industry (MII) of the People's Republic of China. 2006-12
Mobile phones General Applications Application development · Application distribution · Banking · Blogging · Commerce · Content · Gambling · Gaming · Health · Instant messaging · Learning · Local search · Location tracking · Marketing · MMS · Music · News · Payment · Publishing · Push e-mail · SMS · Telephony · Text messaging · Ticketing · Web · Cloud computingCulture Devices Environmental health Law Networking Channel capacity · Frequencies · Network operators · Signal · SIM · Standards comparison · VoIP · WAP · XHTML-MP
Generations: 0G · 1G · 2G · 3G · 4G · 5GCategories:- Mobile phones
- Mobile telecommunications
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.