- Spin column-based nucleic acid purification
-
Column-based nucleic acid purification is a solid phase extraction method to quickly purify nucleic acids.
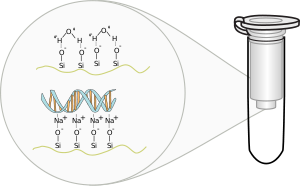
This method relies on the fact that the nucleic acid may bind (adsorption) to the solid phase (silica or other) depending on the pH and the salt content of the buffer, which may be a Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer or Phosphate buffer (used in DNA microarray experiments due to the reactive amines).
Therefore, three stages are:- The sample is added to the column and the nucleic acid binds due to the lower pH (relative to the silanol groups on the column) and salt concentration of the binding solution, which may contain buffer, a denaturing agent (such as guanidine hydrochloride), Triton X-100, isopropanol and a pH indicator
- The column is then washed (5 mM KPO4 pH 8.0 or similar, 80% EtOH)
- The column can be eluted with buffer or simply water
Even prior to the major techniques employed today it was known that in the presence of chaotropic agents, such as sodium iodide or sodium perchlorate, DNA binds to silica, glass particles or to unicellular algae called diatoms which shield their cell walls with silica. This property was used to purify nucleic acid using glass powder or silica beads under alkaline conditions. [1] This was later improved used guanidinium thiocyanate or guanidinium hydrochloride as the chaotropic agent. [2] The use of beads was later changed to minicolumns.
- For explanation of how the silicon and DNA bind see separation by silica adsorption
See also
- Guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction
- Ethanol precipitation
- DNA separation by silica adsorption
References
- ^ Marko MA, Chipperfield R, Birnboim HC. A procedure for the large-scale isolation of highly purified plasmid DNA using alkaline extraction and binding to glass powder. Anal Biochem. 1982 Apr;121(2):382-7. PMID: 6179438
- ^ Boom R, Sol CJ, Salimans MM, Jansen CL, Wertheim-van Dillen PM, van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495-503. PMID: 1691208
Molecular biology Overview Element(Genetic • Heredity)
Promoter (Pribnow box, TATA box) • Operon (gal operon, lac operon, trp operon) • Intron • Exon • Terminator • Enhancer • Repressor (lac repressor, trp repressor) • Silencer • Histone methylationLinked LifeEngineering Conceptmitosis • cell signalling • Post-transcriptional modification and Post-translational modification • Dry Lab/Wet labTechniqueCell culture • model organisms (such as C57BL/6 mice) • method (Nucleic acid • Protein) • Fluorescence, Pigment & Radioactivity
- High-throughput Technique (-omics): DNA microarray • Mass spectrometry • Lab-on-a-chip
Categories:- Biochemistry methods
- Molecular biology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.