- Omenn syndrome
-
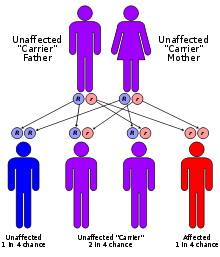
Omenn syndrome Classification and external resources ICD-10 D81.2 (ILDS D81.210) OMIM 603554 DiseasesDB 32676 eMedicine ped/1640 Omenn syndrome is an autosomal recessive severe combined immunodeficiency[1] associated with mutations in the recombination activating genes (RAG1 and RAG2), affecting circulating levels of both B-cells and T-cells.
Contents
Symptoms
The symptoms are very similar to graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). This is because the patients have some T cells with limited levels of recombination with the mutant RAG genes. These T cells are abnormal and have a very specific affinity for self antigens found in the thymus and in the periphery. Therefore, these T cells are auto-reactive and cause the GVHD phenotype.
Symptoms include:
- Desquamation (shedding the outer layers of skin)
- Chronic diarrhea
- Erythroderma (widespread reddening of the skin)
- Hepatosplenomegaly (simultaneous enlargement of both the liver and the spleen)
- Leukocytosis (elevation of the white blood cell count)
- Lymphadenopathy (swelling of one or more lymph nodes)
- Persistent bacterial infections
- Elevated serum IgE
Genetics
Treatment
Omenn syndrome is sometimes treated with bone marrow transplantation and cord blood stem cells.
See also
References
- ^ Santagata S, Villa A, Sobacchi C, Cortes P, Vezzoni P (2000). "The genetic and biochemical basis of Omenn syndrome". Immunol Rev. 178: 64–74. doi:10.1034/j.1600-065X.2000.17818.x. PMID 11213808.
Immune disorders: Lymphoid and complement immunodeficiency (D80–D85, 279.0–4) Primary IgA deficiency · IgG deficiency · IgM deficiency · Hyper IgM syndrome (2, 3, 4, 5) · Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome · Hyper-IgE syndromeOtherthymic hypoplasia: hypoparathyroid (Di George's syndrome) · euparathyroid (Nezelof syndrome, Ataxia telangiectasia)x-linked: X-SCID
autosomal: Adenosine deaminase deficiency · Omenn syndrome · ZAP70 deficiency · Bare lymphocyte syndromeAcquired Leukopenia:
LymphocytopeniaComplement deficiency C1-inhibitor (Angioedema/Hereditary angioedema) · Complement 2 deficiency/Complement 4 deficiency · MBL deficiency · Properdin deficiency · Complement 3 deficiency · Terminal complement pathway deficiency · Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria · Complement receptor deficiencyCategories:- Rare diseases
- Syndromes
- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Hepatology
- Noninfectious immunodeficiency-related cutaneous conditions
- Combined T and B–cell immunodeficiencies
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.