- Counties of Sweden
-
Kingdom of Sweden 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
SwedenMonarchyParliamentJudiciaryDivisionsForeign relationsRelated articles

Sweden's administrationCounties of Sweden: Municipalities of Sweden: See also: - Riksområden
- NUTS of Sweden
- ISO 3166-2:SE
The Counties of Sweden (Swedish: län) are the first level administrative and political subdivisions of Sweden. Sweden is divided into 21 counties. The counties were established in 1634 on Count Axel Oxenstierna's initiative, superseding the historical provinces of Sweden (Swedish: landskap) to introduce a modern administration. At that time, they were what the translation of län into English literally means; fiefdoms. The county borders often trail the provincial borders, but the Crown often chose to make slight relocations to suit their purposes. There are controversial proposals to divide Sweden into larger regions, replacing the current counties.
Contents
Function
In each county there is a County Administrative Board (länsstyrelse) headed by a governor (landshövding) as well as a County Council and several other government organisations.
The County Administrative Board is appointed by the Government to coordinate administration with national political goals for the county.
The county council or landsting on the other hand is a regional government, i.e. a political assembly appointed by the electorate to deliberate on the municipal affairs of the county, primarily regarding the public healthcare system and also public transport, education and culture.
A number of several other government agencies are organised on a county basis, including the main bodies of police, employment, social insurance, and forestry services.
Map
With official county codes.
- AB: Stockholm County
- AC: Västerbotten County
- BD: Norrbotten County
- C: Uppsala County
- D: Södermanland County
- E: Östergötland County
- F: Jönköping County
- G: Kronoberg County
- H: Kalmar County
- I: Gotland County
- K: Blekinge County
- M: Skåne County
- N: Halland County
- O: Västra Götaland County
- S: Värmland County
- T: Örebro County
- U: Västmanland County
- W: Dalarna County
- X: Gävleborg County
- Y: Västernorrland County
- Z: Jämtland County
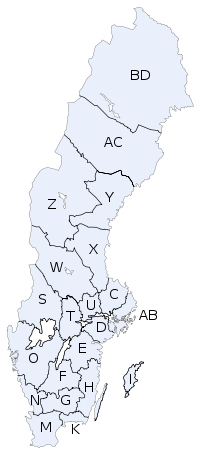
Counties of Sweden 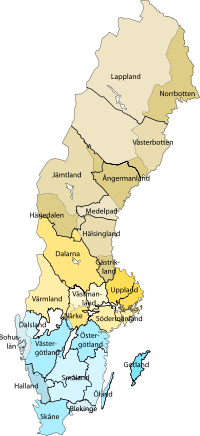
Comparing with provinces of Sweden, one sees many similarities. Bold lines are counties, colors are provinces. Each county is further divided into municipalities (kommuner), the existence of which is partly at the discretion of the central government. Since 2004 their number has been 290, thus an average of 13.8 municipalities per county. (See Municipalities of Sweden)
Until 1968, the City of Stockholm had its own "county code" A, which is still used interchangeably with AB in some contexts.
And County of Stockholm had county code B.
History
Older subdivisions
The provinces of Sweden, or landskap, and the lands of Sweden, or landsdelar, lack political importance today but are common denominations culturally and historally. The provinces had their own laws and justice system and could have large cultural and religious differences. Note that the province of Småland (literally small lands) historically was several provinces with its own laws. Here burial tradition in the era before the Viking age could differ significantly from province to province. The province of Norrbotten is a relatively recent creation; it was part of Västerbotten which extended all the way to Österbotten into today's Finland before 1809. Finnish and Swedish Lappland was also one province until 1809.
Historically, the provinces were divided into three lands: Götaland, being southern and western Sweden; Svealand being eastern and south-eastern, and Norrland being the entire northern half. The names of the first two refer to ancient tribes, and the third is a geographical reference. They are still commonly used as geographical references. The boundaries have changed over time, with the most significant in 1658(the cession of provinces from Denmark-Norway to Sweden) and 1812(due to the loss of Finland to Russia in 1809). In 1812 some provinces were moved from Götaland to Svealand.
Finland
After the Finnish War, Sweden was forced to cede the counties in Finland to Russia following the Treaty of Fredrikshamn in (1809). However, the counties were upheld in Finland until a reform in 1997. They are still in use in Sweden, 370 years hence.
The counties in Finland established in 1634 were: Turku and Pori County, Nyland and Tavastehus County, Viborg and Nyslott County, Ostrobothnia County and Kexholm County. Over time the number of subdivisions in Finland increased to twelve, until a reorganization in 1997 reduced their number to six provinces, while keeping the administrative model intact. The counties in Finland were abolished in 2010.
Abolished counties
Abolished counties in current day Sweden proper are:
- Skaraborg County + Gothenburg and Bohus County + Älvsborg County (merged as Västra Götaland County in 1999)
- Kopparberg County (became Dalarna County in 1999)
- Malmöhus County + Kristianstad County (merged as Skåne County in 1997)
- Norrland County (in 1645 divided into Västerbotten County, Hudiksvall County and Härnösand County)
- Nyköping County, Gripsholm County and Eskilstunahus County (united in 1683 to become Södermanland County)
- Närke County (became Örebro County)
- Härnösand County (1645–1654, formed Västernorrland County)
- Hudiksvall County (1645–1654, formed Gävleborg County)
- Stockholm Överståtshållarämbete (1634-1967, united with Stockholm County)
- Svartsjö County (1786–1809, united with Stockholm County)
- Öland County (1819–1826, united with Kalmar County)
Proposed regions
Under the aegis of the Swedish government, Ansvarskommittén has been investigating the possibilities of merging the current 21 counties into 6 to 9 larger regions. If approved, these would come into effect around 2015. These suggestions of new regions were found in their final report:[1]
A model for this comes from the merger of some counties into Skåne County and Västra Götaland County in 1997 and 1998, respectively, which is now considered a success.
The counties are discussing the proposal. An obstacle is that Stockholm County does not want to merge with any other county, while its neighbours want to merge with Stockholm.
Riksområden
The European Union is divided into a Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics where the counties in Sweden correspond to the third level of division. For the purpose of creating regions corresponding to the second level, counties have been grouped into eight Riksområden, or National Areas: Stockholm, East Middle Sweden, North Middle Sweden, Middle Norrland, Upper Norrland, Småland and the islands, West Sweden and South Sweden.
See also
References
External links
- The Swedish County Administrative Boards
- Official site of the Swedish government
- National Atlas of Sweden (searchable)
First-level administrative divisions in Europe Sovereign
statesAlbania · Andorra · Armenia2 · Austria · Azerbaijan3 · Belarus · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Cyprus2 · Czech Republic · Denmark · Estonia · Finland · France1 · Georgia3 · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland · Ireland · Italy · Kazakhstan2 · Latvia · Liechtenstein · Lithuania · Luxembourg · Republic of Macedonia · Malta · Moldova · Monaco · Montenegro · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russia1 · San Marino · Serbia · Slovakia · Slovenia · Spain · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey1 · Ukraine · United Kingdom
States with limited
recognitionAbkhazia3 · Kosovo · Northern Cyprus2 · South Ossetia3
1 Has part of its territory outside Europe. 2 Considered European for cultural, political and historical reasons but is geographically in West Asia. 3 Partially or entirely in Asia, depending on the definition of the border.Categories:- Counties of Sweden
- Subdivisions of Sweden
- Lists of country subdivisions
- Country subdivisions of Europe
- First-level administrative country subdivisions
- Sweden-related lists
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.