- Chain drive
-
 Roller chain and sprocket
Roller chain and sprocketChain drive is a way of transmitting mechanical power from one place to another. It is often used to convey power to the wheels of a vehicle, particularly bicycles and motorcycles. It is also used in a wide variety of machines besides vehicles.
Most often, the power is conveyed by a roller chain, known as the drive chain or transmission chain,[1] passing over a sprocket gear, with the teeth of the gear meshing with the holes in the links of the chain. The gear is turned, and this pulls the chain putting mechanical force into the system. Another type of drive chain is the Morse chain, invented by the Morse Chain Company of Ithaca, New York, USA. This has inverted teeth. [2]
Sometimes the power is output by simply rotating the chain, which can be used to lift or drag objects. In other situations, a second gear is placed and the power is recovered by attaching shafts or hubs to this gear. Though drive chains are often simple oval loops, they can also go around corners by placing more than two gears along the chain; gears that do not put power into the system or transmit it out are generally known as idler-wheels. By varying the diameter of the input and output gears with respect to each other, the gear ratio can be altered, so that, for example, the pedals of a bicycle can spin all the way around more than once for every rotation of the gear that drives the wheels.
Contents
History
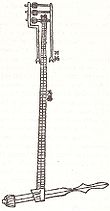 Oldest known illustration of an endless power-transmitting chain drive, from Su Song's book of 1092 describing his clock tower of Kaifeng
Oldest known illustration of an endless power-transmitting chain drive, from Su Song's book of 1092 describing his clock tower of Kaifeng
The oldest known application of a chain drive appears in the Polybolos, a repeating crossbow described by the Greek engineer Philon of Byzantium (3rd century BC). Two flat-linked chains were connected to a windlass, which by winding back and forth would automatically fire the machine's arrows until its magazine was empty.[3] Although the device did not transmit power continuously since the chains "did not transmit power from shaft to shaft",[4] the Greek design marks the beginning of the history of the chain drive since "no earlier instance of such a cam is known, and none as complex is known until the 16th century. It is here that the flat-link chain, often attributed to Leonardo da Vinci, actually made its first appearance."[3]
The first continuous power-transmitting chain drive was depicted in the written horological treatise of the Song Dynasty (960–1279) Chinese engineer Su Song (1020-1101 AD), who used it to operate the armillary sphere of his astronomical clock tower as well as the clock jack figurines presenting the time of day by mechanically banging gongs and drums.[5][6] The chain drive itself was given power via the hydraulic works of Su's water clock tank and waterwheel, the latter which acted as a large gear.
The endless power-transmitting chain drive was invented separately in Europe by Jacques de Vaucanson in 1770 for a silk reeling and throwing mill.[6] J. F. Tretz was the first to apply the chain drive to the bicycle in 1869.[6]
Chains versus belts
Drive chains are most often made of metal, while belts are often rubber, plastic, or other substances. Although well-made chains may prove stronger than belts, their greater mass increases drive train inertia.
Drive belts can often slip (unless they have teeth) which means that the output side may not rotate at a precise speed, and some work gets lost to the friction of the belt against its rollers. Teeth on toothed drive belts generally wear faster than links on chains, but wear on rubber or plastic belts and their teeth is often easier to observe; you can often tell a belt is wearing out and about to break more easily than a chain.
Conventional roller chain drives suffer the potential for vibration, as the effective radius of action in a chain and sprocket combination constantly changes during revolution. If the chain moves at constant speed, then the shafts must accelerate and decellerate constantly. If a drive sprocket rotates at constant RPM, then the chain (and probably the driven sprocket) must accelerate and decellerate constantly. This is usually not an issue with many drive systems, however most motorcycles are fitted with a rubber bushed rear wheel hub to virtually eliminate this vibration issue. Toothed belt drives are designed to avoid this issue by operating at a constant pitch radius.
Chains are often narrower than belts, and this can make it easier to shift them to larger or smaller gears in order to vary the gear ratio. Multi-speed bicycles with derailleurs make use of this. Also, the more positive meshing of a chain can make it easier to build gears that can increase or shrink in diameter, again altering the gear ratio.
Both can be used to move objects by attaching pockets, buckets, or frames to them; chains are often used to move things vertically by holding them in frames, as in industrial toasters, while belts are good at moving things horizontally in the form of conveyor belts. It is not unusual for the systems to be used in combination; for example the rollers that drive conveyor belts are themselves often driven by drive chains.
Drive shafts are another common method used to move mechanical power around that is sometimes evaluated in comparison to chain drive; in particular shaft drive versus chain drive is a key design decision for most motorcycles. Drive shafts tend to be even tougher and more reliable than chain drive, but weigh even more (robbing more power), and impart rotational torque. Virtually all high performance motorcycles use chain drive, with shaft driven arrangements generally used for many non-sporting machines. Toothed belt drives are used for many lower power motorcycles.
Use in vehicles
Bicycles
Main article: Bicycle chainChain drive was the main feature which differentiated the safety bicycle introduced in 1885, with its two equal-sized wheels, from the direct-drive penny-farthing or "high wheeler" type of bicycle. The popularity of the chain-driven safety bicycle brought about the demise of the penny-farthing, and is still a basic feature of bicycle design today.
Automobiles
Transmitting power to the wheels
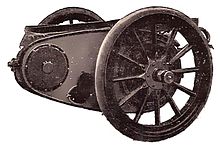
Chain drive was a popular power transmission system from the earliest days of the automobile. It gained prominence as an alternative to the Système Panhard with its rigid Hotchkiss driveshaft and universal joints.
A chain-drive system uses one or more roller chains to transmit power from a differential to the rear axle. This system allowed for a great deal of vertical axle movement (for example, over bumps), and was simpler to design and build than a rigid driveshaft in a workable suspension. Also, it had less unsprung weight at the rear wheels than the Hotchkiss drive, which would have had the weight of the driveshaft to carry as well, which in turn meant that the tires would last longer.
Frazer Nash were strong proponents of this system using one chain per gear selected by dog clutches. The Frazer Nash chain drive system, (designed for the GN Cyclecar Company by Archibald Frazer-Nash and Henry Ronald Godfrey) was very effective, allowing extremely fast gear selections. The Frazer Nash (or GN) transmission system provided the basis for many "special" racing cars of the 1920s and 1930s, the most famous being Basil Davenport's Spider which held the outright record at the Shelsley Walsh Speed Hill Climb in the 1920s.
Parry-Thomas was killed during a land speed record attempt in his car 'Babs' when the chain final-drive broke, decapitating him.
The last popular chain drive automobile was the Honda S600 of the 1960s.
Inside motors
Internal combustion engines often use chain drive to power the timing chain used to drive overhead camshaft valvetrains. This is an area in which chain drives frequently compete directly with belt drive systems, and an excellent example of some of the differences and similarities between the two approaches. For this application, chains last longer, but are often harder to replace. Being heavier, the chain robs more power, but is also less likely to fail. The camshaft of a four stroke engine must rotate at half crankshaft speed, so some form of reduction gearing is needed and a direct drive from the crankshaft isn't possible. Alternatives to chain drives include gear trains, bevel gear and shaft drives, or toothed flexible belt drives.
Transfer cases
Today, inverted tooth drive chains are commonly used in passenger car and light truck transfer cases. Transfer case
Motorcycles
Chain drive versus belt drive or use of a driveshaft is a fundamental design decision in motorcycle design; nearly all motorcycles use one of these three designs. See Motorcycle construction for more details.
See also
References
- ^ Green 1996, pp. 2337–2361
- ^ Cross & Morse in Birmingham, http://www.crossmorse.com
- ^ a b Werner Soedel, Vernard Foley: Ancient Catapults, Scientific American, Vol. 240, No. 3 (March 1979), p.124-125
- ^ Needham, Joseph (1986). Science and Civilization in China: Volume 4, Part 2, Mechanical Engineering. Cave Books, Ltd. Page 109.
- ^ Needham, Joseph (1986). Science and Civilization in China: Volume 4, Part 2, Mechanical Engineering. Cave Books, Ltd. Page 111, 165, 456–457.
- ^ a b c Temple, Robert. (1986). The Genius of China: 3,000 Years of Science, Discovery, and Invention. With a forward by Joseph Needham. New York: Simon and Schuster, Inc. ISBN 0-671-62028-2. Page 72.
Bibliography
- Green, Robert E. et al. (eds) (1996), Machinery's Handbook (25 ed.), New York, NY, USA: Industrial Press, ISBN 978-0-8311-2575-2, http://www.worldcat.org/title/machinerys-handbook/oclc/473691581.
External links
Gear systems Spur gear systems • Worm drive • Rack and pinion • Epicyclic (planetary) gearing • Sun and planet gear • Harmonic drive • Cycloidal drive • Non-circular gearGear shapes Geartooth profiles Gear mechanics Examples In Bicycles: Cogset • Derailleur gears • Hub gear • Shaft-driven bicycle • Sprocket
In Horology: Wheel trainSee also Ball screw • Leadscrew • Jackscrew • Belt drive • Chain drive • Gear manufacturing • Freewheel • Lego Technic • Spur gear corrected toothMotorcycle components Chassis 
Engine Layouts (common) Energy source Unconventional Transmission Final drive Accessories Other Categories:- Mechanics
- Automotive transmission technologies
- Mechanical power transmission
- Mechanical power control
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.