- Oxalyl chloride
-
Oxalyl chloride 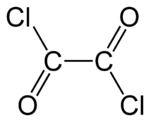

 Oxalyl dichlorideOther namesEthanedioyl dichloride
Oxalyl dichlorideOther namesEthanedioyl dichloride
Oxalic acid chloride
Oxalic acid dichloride
Oxalyl dichloride
Oxalic dichloride
Oxaloyl chlorideIdentifiers CAS number 79-37-8 
RTECS number KI2950000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - ClC(=O)C(=O)Cl
Properties Molecular formula C2O2Cl2 Molar mass 126.93 g/mol Appearance colorless liquid Density 1.4785 g/mL, liquid Melting point -16 °C, 257 K, 3 °F
Boiling point 63-64 °C, 336-337 K, 145-147 °F (1.017 bar)
Solubility in water Decomposes Refractive index (nD) 1.429 Hazards MSDS External MSDS EU classification not listed NFPA 704 Related compounds Related acyl chlorides Malonyl chloride
Succinyl chloride
phosgeneRelated compounds Oxalic acid
Diethyl oxalate
Oxamide
Oxalyl hydrazide
Cuprizon 1 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Oxalyl chloride or ethanedioyl dichloride is a chemical compound with the formula (COCl)2. This colourless, sharp-smelling liquid, the diacid chloride of oxalic acid, is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.[1] It can be prepared by treating oxalic acid with phosphorus pentachloride.[2]
Contents
Applications in organic synthesis
Synthesis of acid chlorides
It is mainly used in organic synthesis for the preparation of acid chlorides from the corresponding carboxylic acids. Like thionyl chloride, the reagent produces volatile side products in this application:
Oxalyl chloride tends to be a milder, more selective reagent. A small amount of N,N-dimethylformamide is usually added as a catalyst for the reaction.
Formylation of arenes
Oxalyl chloride reacts with aromatic compounds in the presence of aluminium chloride to give the corresponding acid chloride in a process known as a Friedel-Crafts acylation.[3][4] The resulting acid chloride can be hydrolysed in water to form the corresponding carboxylic acid.
Preparation of diesters
Like other acid chlorides, oxalyl chloride reacts with alcohols to give esters:
- 2 RCH2OH + (COCl)2 → RCH2OC(O)C(O)OCH2R + 2 HCl
Typically, such reactions are conducted in the presence of a base such as pyridine. The diester derived from phenol, phenyl oxalate ester, is Cyalume, the active ingredient in glow sticks.
Oxidation of alcohols
The combination of DMSO, oxalyl chloride, and triethylamine converts alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes and ketones via the process known as the Swern oxidation.
Other
Oxalyl chloride was reportedly used in the first synthesis of dioxane tetraketone (C4O6), a novel oxide of carbon.[5]
Precautions
As with all acyl chlorides, oxalyl chloride reacts with water liberating HCl gas. Overall, its effects are comparable to those of phosgene.
In March 2000, a Malaysia Airlines Airbus A330 was damaged beyond repair after a falsely declared cargo of oxalyl chloride leaked into the cargo bay. [6]
References
- ^ Salmon, R. "Oxalyl Chloride" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001, John Wiley & Sons, New York, doi:10.1002/047084289X.ro015.
- ^ Vogel, A.; Steffan, G.; Mannes, K.; Trescher, V. "Oxalyl chloride" DE 78-2840435 19780916.Chemical Abstracts Number 93:94818
- ^ Neubert, M. E.; Fishel, D. L. (1990), "Preparation of 4-Alkyl- and 4-Halobenzoyl Chlorides: 4-Pentylbenzoyl Chloride", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv7p0420; Coll. Vol. 7: 420
- ^ Sokol, P. E. (1973), "Mesitoic Acid", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV5P0706; Coll. Vol. 5: 706
- ^ Paolo Strazzolini, Alberto Gambi, Angelo G. Giumanini and Hrvoj Vancik (1998). "The reaction between ethanedioyl (oxalyl) dihalides and Ag2C2O4: a route to Staudinger’s elusive ethanedioic (oxalic) acid anhydride". J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 (16): 2553–2558. doi:10.1039/a803430c.
- ^ "Firm told to pay $65 mln for ruining plane". Reuters. 2007-12-06. http://www.reuters.com/article/oddlyEnoughNews/idUSN0620441720071206. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
Categories:- Acyl chlorides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

