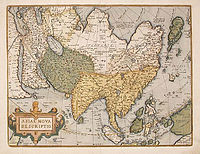
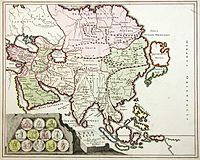
- Cartography of Asia
-
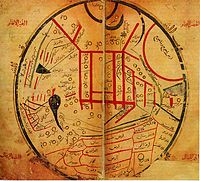 Map from Mahmud al-Kashgari's Diwanu Lughat at-Turk, showing the 11th century distribution of Turkic tribes.
Map from Mahmud al-Kashgari's Diwanu Lughat at-Turk, showing the 11th century distribution of Turkic tribes.
Contents
Antiquity
Babylon in Southwest Asia is at the center of the very earliest world maps, beginning with the Babylonian world map in the 6th century BC; it is a clay tablet 'localized' world map of Babylon, rivers, encircling ocean, and terrain, surrounded by 'islands' in a 7-star format. In classical Greek geography, "Asia" is one of three major landmasses, besides Europe and Libya. Asia is given higher resolution in Hellenistic geography, in particular on Ptolemy world map. Cartography of India begins with early charts for navigation[1] and constructional plans for buildings.[2] Chinese geography from the 2nd century BC (Han dynasty) becomes aware of Turkestan, where Hellenistic Greek and Han Chinese spheres of influence overlap.
Middle Ages
In medieval T and O maps, Asia makes for half the world's landmass, with Africa and Europe accounting for a quarter each. With the High Middle Ages, Southwest and Central Asia receive better resolution in Muslim geography, and the 11th century map by Mahmud al-Kashgari is the first world map drawn from a Central Asian point of view. In the same period, European explorers of the Silk road like William Rubruck and Marco Polo increase geographical knowledge of Asia in the west, in particular establishing that the Caspian Sea is not connected to the northern ocean.
Chinese exploration by medieval times extends Chinese geographical knowledge to the Indian ocean, the Arabian peninsula and East Africa as well as Southeast Asia.
Age of exploration
European maps of Asia become much more detailed from the 15th century, the 1459 Fra Mauro map showing a reasonable complete picture, including correctly placed Korea and Japan.
Modern maps
The modern map making techniques in India, like other parts of the world, employ digitization, photographic surveys and printing.[3] Satellite imageries, aerial photographs and video surveying techniques are also used.[3]
Notes
- ^ Sircar, page 330
- ^ Gole 1990
- ^ a b Indian Express (1999). Modern map-making techniques on display. Indian Express Newspapers (Bombay) Ltd.
References
- Gole, S. Size as a Measure of Importance in Indian Cartography. Imago Mundi, Vol. 42, (1990), pp. 99-105.
- Sircar, D.C.C. (1990). Studies in the Geography of Ancient and Medieval India. Motilal Banarsidass Publishers. ISBN 8120806905.
Literature
- Harley and Woodward (eds.), The History of Cartography. Vol. 2. bk 2, Cartography in Traditional East and Southeast Asian Societies, University of Chicago Press (1994), ISBN 978-0226316376.
- Kenneth Nebenzahl, Mapping the Silk Road and Beyond, ISBN 0714844098.
See also
- Geography of Asia
- Muslim geography
- Chinese geography
- Chinese exploration
- Cartography of India
- History of cartography
- History of geography
- Exploration of Asia
- Cartography of Europe
- Cartography of Africa
- Boundaries between continents
External links
- Historical maps of Asia, Alabama Maps project of the Cartographic Research Laboratory, University of Alabama.
- Asia Historical Maps, Perry-Castañeda Library Map Collection, University of Texas, Austin.
Maps of Asia Sovereign
states- Afghanistan
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Brunei
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Cambodia
- People's Republic of China
- Cyprus
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Egypt
- Georgia
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Japan
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Lebanon
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Qatar
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
- Syria
- Tajikistan
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- United Arab Emirates
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
- Yemen
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- Palestine
- Republic of China (Taiwan)
- South Ossetia
Dependencies and
other territories- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Hong Kong
- Macau
Categories:- Cartography stubs
- Maps of Asia
- Geography of Asia
- Cartography
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.