- Cartography of Africa
-
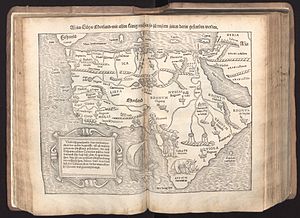 Map of Africa from Sebastian Münster's Cosmographia (1545). The map legend mentions the route for spice trade discovered "in our times" (zů unsern zeiten) from Spain via the Canaries and the Cape of Good Hope on to Callicut.
Map of Africa from Sebastian Münster's Cosmographia (1545). The map legend mentions the route for spice trade discovered "in our times" (zů unsern zeiten) from Spain via the Canaries and the Cape of Good Hope on to Callicut.
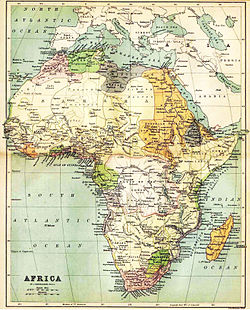 1885 map of Africa by John Bartholomew, showing the situation on the eve of the European scramble for Africa. States shown include Alaouite Morocco, Ottoman Algeria, Tunis, Tripolitania and Egypt, Abyssinia, and in the south Cape Colony, Orange Free State and Transvaal. Detail shown in the interior of the continent is based on then-recent expeditions, such as the exploration of Lake Victoria by Henry Morton Stanley in 1871.
1885 map of Africa by John Bartholomew, showing the situation on the eve of the European scramble for Africa. States shown include Alaouite Morocco, Ottoman Algeria, Tunis, Tripolitania and Egypt, Abyssinia, and in the south Cape Colony, Orange Free State and Transvaal. Detail shown in the interior of the continent is based on then-recent expeditions, such as the exploration of Lake Victoria by Henry Morton Stanley in 1871.
The earliest cartographic depictions of Africa are found in early world maps. In classical antiquity, Africa (also Libya) was assumed to cover the quarter of the globe south of the Mediterranean, an arrangement that was adhered to in medieval T and O maps. The only part of Africa well known in antiquity was the coast of North Africa, described in Greek periplus from the 6th century BC. Hellenistic era geographers defined Egypt as part of Asia, taking the boundary of Asia and Egypt to lie at the Catabathmus Magnus (the escarpment of Akabah el-Kebir in western Egypt). Ptolemy's world map (2nd century) shows a reasonable awareness of the general topography of North Africa, but is unaware of anything south of the equator. The limit of Ptolemy's knowledge in the west is Cape Spartel (35° 48′ N); while he does assume that the coast eventually retreats in a "Great Gulf of the Western Ocean", this is not likely based on any knowledge of the Gulf of Guinea.[1] In the east, Ptolemy is aware of the Red Sea (Sinus Arabicus) and the protrusion of the Horn of Africa, describing the gulf south of the Horn of Africa as Sinus Barbaricus.
With the European exploration of Africa from the 15th century, maps of Africa became more precise. The Fra Mauro map of 1459 shows a more detailed picture of Africa as a continent, including the Cape of Diab at its southernmost point, reflecting an expedition of 1420. Sebastian Münster's Cosmographia (1545) labels the Cape of Good Hope, reached by Bartolomeu Dias in 1488, as caput bonae spei. The interior of Africa was not mapped in any detail before the second half of the 19th century.
References
See also
Categories:- Cartography stubs
- Cartography
- Geography of Africa
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
