- Raspberry ketone
-
Raspberry ketone[1] 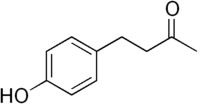 4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) butan- 2-oneOther namesFrambinone
4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) butan- 2-oneOther namesFrambinone
Oxyphenylon
Rheosmin
RasketoneIdentifiers Abbreviations RK CAS number 5471-51-2 PubChem 21648 ChemSpider 20347 
EC number 226-806-4 ChEMBL CHEMBL105912 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(CCc1ccc(O)cc1)C
Properties Molecular formula C10H12O2 Molar mass 164.2 g mol−1 Appearance White needles[2] Melting point 82-84 °C
Boiling point 140-146 °C (at 0.5 mmHg)
Hazards R-phrases R22  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Raspberry ketone is a natural phenolic compound that is the primary aroma compound of red raspberries. It is used in perfumery, in cosmetics, and as a food additive to impart a fruity odor. It is one of the most expensive natural flavor components used in the food industry. The natural compound can cost as much as $20,000 per kg.[3] In 1965, the Food and Drug Administration placed raspberry ketone on generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status.[4]
In plants, raspberry ketone is synthesized from coumaroyl-CoA.[5] Extraction of pure raspberry ketone is usually 1-4 mg per kg of raspberries.[3]
Since the natural abundance of raspberry ketone is very low, it is prepared industrially by a variety of methods from chemical intermediates.[6] One of the ways this can be done is through a crossed aldol-catalytic hydrogenation. In acetone and sodium hydroxide, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde can form the α,β-unsaturated ketone. This then goes through catalytic hydrogenation to produce raspberry ketone. This method produces a 99% yield.[7]
When given to mice in high doses (up to 2% of food intake), raspberry ketone has been shown to prevent high-fat-diet-induced elevations in body weight.[8] This effect is reported to stem from the alteration of lipid metabolism, increasing norepinephrine-induced lipolysis. Although products containing this compound are marketed for weight loss, this effect has not been studied in humans.
References
- ^ Catalog of Organics and Fine Chemicals, Acros Organics, 2004/05, page 1250.
- ^ Opdyke, D. L. J. (1978). "4-(p-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone". Fd. Cosmet. Toxicol. 16: 781–782. doi:10.1016/S0015-6264(78)80113-8.
- ^ a b Beekwilder, J.; Van der Meer, I.; Sibbesen, O.; Broekgaarden, M.; Qvist, I.; Mikkelsen, J.; Hall, R. (2007). "Microbial production of natural raspberry ketone". Biotechnol. J. 2 (10): 1270–1279. doi:10.1002/biot.200700076. PMID 17722151.
- ^ Opdyke, D. L. J. 4-(p-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone. Fd. Cosmet. Toxicol. 1978, 16, 781-782.
- ^ MetaCyc Pathway: raspberry ketone biosynthesis
- ^ Tateiwa, J.-I., Horiuchi, H., Hashimoto, K., Yamauchi, T., and Uemura, S. (1994). "Cation-exchanged montmorillonite-catalyzed facile Friedel-crafts alkylation of hydroxy and methoxy aromatics with 4-hydroxybutan-2-one to produce raspberry ketone and some pharmaceutically active compounds". J. Org. Chem. 59 (20): 5901–5904. doi:10.1021/jo00099a017.
- ^ Smith, L. R. (1996). "Rheosmin (“Raspberry Ketone”) and Zingerone, and Their Preparation by Crossed Aldol-Catalytic Hydrogenation Sequences". The Chemical Educator 1 (3): 1–18. doi:10.1007/s00897960034a.
- ^ Morimoto C, Satoh Y, Hara M, Inoue S, Tsujita T, Okuda H (2005). "Anti-obese action of raspberry ketone". Life Sci. 77 (2): 194–204. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2004.12.029. PMID 15862604.
Categories:- Flavors
- Food additives
- Ketones
- Perfume ingredients
- Natural phenols
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
