- 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
-
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde 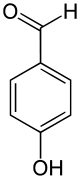 4-HydroxybenzaldehydeOther namesp-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
4-HydroxybenzaldehydeOther namesp-HydroxybenzaldehydeIdentifiers CAS number 123-08-0 
PubChem 126 ChemSpider 123 
UNII O1738X3Y38 
DrugBank DB03560 KEGG C00633 
ChEBI CHEBI:17597 
ChEMBL CHEMBL14193 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=Cc1ccc(O)cc1
Properties Molecular formula C7H6O2 Molar mass 122.12 g mol−1 Appearance yellow to tan powder Density 1.226 ± 0.06 g/cm3 Melting point 112-116 °C
Boiling point 310-311 °C
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. It can be found in the orchid Gastrodia elata[1].
Contents
Chemistry
The Dakin oxidation is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidized, and the hydrogen peroxide is reduced.
Metabolism
p-hydroxybenzaldehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme found in carrots (Daucus carota)[2].
See also
- Salicylaldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde)
- 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
References
- ^ 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde from Gastrodia elata B1. is active in the antioxidation and GABAergic neuromodulation of the rat brain. Jeoung-Hee Ha, Dong-Ung Lee, Jae-Tae Lee, Jin-Sook Kim, Chul-Soon Yong, Jung-Ae Kim, Jung-Sang Ha and Keun- Huh, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Volume 73, Issues 1-2, November 2000, Pages 329-333, doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00313-5
- ^ Evidence for p-hydroxybenzoate formation involving enzymatic phenylpropanoid side-chain cleavage in hairy roots of Daucus carota. Debabrata Sircar and Adinpunya Mitra, Journal of Plant Physiology, Volume 165, Issue 4, 13 March 2008, Pages 407-414, doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2007.05.005

This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
