- Disilene
-
 Disilenes
Disilenes
Disilenes are compounds containing a silicon–silicon double bond and are considered to be heavier analogues of alkenes. They are sometimes also called disilaalkenes.
Contents
History
The first transient disilene was synthesized in 1972 by D. N. Roark and Garry J. D. Peddle. The first thermally stable disilene, tetramesityldisilene, was isolated in 1981 by Robert West[1].
Properties
Simple disilenes are very reactive species and easily undergo polymerization or other reactions, so their life is very short. To prevent this polymerization and other reactions, bulky substituents are used to stabilize disilenes effectively for long-term survival in dilute solution and even in crystals.
Stable disilenes are generally yellow- or orange-colored crystalline compounds.
The Si=Si double bond lengths of disilenes vary between 2.14 and 2.29 Å and are nearly 5 to 10% shorter than the Si-Si single bond lengths of corresponding disilanes. This rate of bond shortening is less than ca 13% in carbon compounds, but is short enough for true double bond characteristics.
A further peculiarity of disilenes is the trans-bending of the substituents, which is never observed in alkenes. The trans-bent angles of disilenes between the R2Si planes and the Si=Si vector range from 0 to 33.8 deg. This is rationalized by the stability of the corresponding silylene fragments. The valence orbitals of silicon are 3s and 3p, while those of carbon are 2s and 2p, so the energy gap between the ns and np orbitals of a silicon atom is larger than that of a carbon atom. Therefore, silylene fragments are in a singlet state, while carbene fragments are in a triplet state. So, when double bonds are formed by the interaction of these two fragments, disilenes which consist of two silylene units are trans-bending and alkenes which consist of two carbene units are planar.
Synthesis
Disilenes are generally synthesized by reduction of 1,2-dihalodisilane, by retro-Diels–Alder fragmentation, by dimerization of silylenes, by photofragmentation of cyclopolysilanes, or by rearrangement of silylsilylenes.
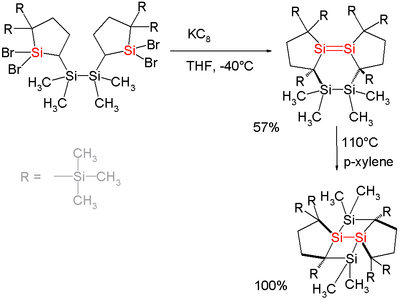
In one study [2] a disilene is prepared by an intramolecular coupling of a 1,1-dibromosilane with potassium graphite. The silicon double bond in the resulting compound has a bond length of 227 picometer (second largest ever found) with trans-bent angles 33° and 31° (by X-ray diffraction).
In addition to this the substituents around the Si-Si bond are twisted by 43°. The disilene isomerizes to a tetracyclic compound by heating at 110°C in xylene thereby releasing its strain energy.See also
References
- ^ West, R.; Fink, M. J.; Michl, J. Tetramesityldisilene, a Stable Compound Containing a Silicon-Silicon Double Bond Science 1981, Vol.214, Issue.4527 P1343.
- ^ Fused Tricyclic Disilenes with Highly Strained Si-Si Double Bonds: Addition of a Si-Si Single Bond to a Si-Si Double Bond Ryoji Tanaka, Takeaki Iwamoto, and Mitsuo Kira Angewandte Chemie International Edition Volume 45, Issue 38 , Pages 6371 - 6373 2006 doi:10.1002/anie.200602214
Categories:- Organosilicon compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.