- Disilyne
-
Disilyne 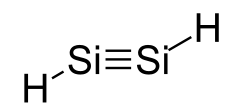 DisilyneOther namesDisilyn
DisilyneOther namesDisilynIdentifiers CAS number 36835-58-2 ChemSpider 16341537 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [SiH]#[SiH]
- InChI=1S/H2Si2/c1-2/h1-2H
Key: NWEREQWWNYLPTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Properties Molecular formula H2Si2 Molar mass 58.19 g mol−1 Exact mass 57.969503130 g mol-1 Related compounds Related silyls Silylene
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references A disilyne is a chemical compound that contains a formal silicon - silicon triple bond and as such is formulated R2Si2 (where R is a substituent group) and is the silicon analogue of an alkyne. The hypothetical parent hydride, Si2H2 does not actually exist, all attempts to synthesize it results in a diradical disilene, with the systematic name of disilene-1,2-diyl. This compound readily tautomerises to disilenylidene. Some chemists use the term silyne to refer to compounds containing a silicon-silicon triple bond [1] whilst others[2] use the term to refer to compounds containing a silicon-carbon triple bond by analogy to silene which often refers to compounds containing silicon- carbon double bonds.[3] The term polysilyne can refer to the layer polymer (SiH)n or substituted derivatives.[1]
Contents
The first reported disilynes
The first example isolated and characterised by X-ray crystallography is an emerald green crystalline compound reported in 2004.[4] This molecule has the structure:
- R′2R′′Si-Si2-SiR′′R′2
- where R′ = HC(SiMe3)2 and R′′ = i-propyl
It was prepared by the reduction of the related tetrabrominated precursor by potassium graphite (KC8), it is air and moisture sensitive and does not melt or decompose until 128 °C.
Considered as a tetrasila-2-yne derivative the four Si atoms in the chain are not collinear and in this respect the compound differs from the related alkyne. The four silicon atoms in the chain are however perfectly coplanar, the first and fourth silicon atoms are trans to one another, and the angle between the triple bond and the adjacent silicon is 137°. The central triple bond is 206 pm (around 4% shorter than Si-Si double bonds (214pm)) and the other Si-Si single bonds are 237 pm. The colour is believed to be due to a weak π - π* transition.
29Si NMR shows upfield shift 89.9 ppm relative to silyl substituted disilenes. Calculations show a bond order of 2.6. An alternative calculation of the bond order by a different group describes the bonding as essentially due to 2 electron pairs with the other pair in non-bonding orbitals.2.[5][6][7] Reaction of this compound with phenylacetylene produced a 1,2 disilabenzene.[8] Other workers[9] have also reported another related compound which contains a hexasila-3-yne chain:
- R3Si(SiR3)SiMeSi2SiMe(SiR3)SiR3
- where Me = methyl and R = t-butyl
In this the Si-Si triple bond length was calculated as 207 pm.
Comparison to C-C, Ge-Ge, Sn-Sn, Pb-Pb triple bonds
Triple bonded compounds of the heavier members of group 14 have all been prepared, lead in 2000 [10] tin[11] and germanium[12] in 2002. In all of these the substituents attached to the bonded metal atoms are not collinear as in the alkynes but trans bent.
See also
References
- ^ a b Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) Inorganic Chemistry, Elsevier ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ Miriam Karni, Yitzhak Apeloig (January 2002). "The quest for a stable silyne, RSi ≡ CR′. The effect of bulky substituents [1]". Silicon Chemistry 1 (1): 59–65. doi:10.1023/A:1016091614005.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0080379419.
- ^ Akira Sekiguchi, Rei Kinjo, Masaaki Ichinohe (September 2004). "A Stable Compound Containing a Silicon-Silicon Triple Bond". Science 305 (5691): 1755–1757. doi:10.1126/science.1102209. PMID 15375262.[1]
- ^ Carlo A. Pignedoli, Dr., Alessandro Curioni, Dr., Wanda Andreoni, Dr. (2005). "Disproving a Silicon Analog of an Alkyne with the Aid of Topological Analyses of the Electronic Structure and Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Calculations". ChemPhysChem 6 (9): 1795–1799. doi:10.1002/cphc.200500064. PMID 16144004.
- ^ Gernot Frenking, Prof. Dr. , Andreas Krapp, Dipl.-Chem. , Shigeru Nagase, Prof. Dr., Nozomi Takagi, Dr., Akira Sekiguchi, Prof. Dr. (2006). "Comment on Disproving a Silicon Analog of an Alkyne with the Aid of Topological Analyses of the Electronic Structure and Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Calculations". ChemPhysChem 7 (4): 799–800. doi:10.1002/cphc.200500689. PMID 16596606.
- ^ Carlo A. Pignedoli, Dr., Alessandro Curioni, Dr., Wanda Andreoni, Dr. (2006). "Reply to Comment on Disproving a Silicon Analog of an Alkyne with the Aid of Topological Analyses of the Electronic Structure and Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Calculations". ChemPhysChem 7 (4): 801–802. doi:10.1002/cphc.200600025.
- ^ Rei Kinjo, Masaaki Ichinohe, Akira Sekiguchi, Nozomi Takagi, Michinori Sumimoto, Shigeru Nagase (2007). "Reactivity of a Disilyne RSiSiR (R = SiiPr[CH(SiMe3)2]2) toward π-Bonds: Stereospecific Addition and a New Route to an Isolable 1,2-Disilabenzene". J. Am. Chem. Soc 129 (25): 7766–7767,. doi:10.1021/ja072759h+S0002-7863(07)02759-X.
- ^ Nils Wiberg, Prof. Dr., Sham Kumar Vasisht, Gerd Fischer, Peter Mayer (2004). "Disilynes. III [1] A Relatively Stable Disilyne RSiSiR (R = SiMe(SitBu3)2)". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 630 (12): 1823–1828. doi:10.1002/zaac.200400177.
- ^ Pu, L.; Twamley, B.; Power, P. P. (2000). "Synthesis and Characterization of 2,6-Trip2H3C6PbPbC6H3-2,6-Trip2 (Trip = C6H2-2,4,6-i-Pr3): A Stable Heavier Group 14 Element Analogue of an Alkyne". J.Am. Chem. Soc(Communication); 122 (14): 3524–3525. doi:10.1021/ja993346m.
- ^ Phillips, A. D.; Wright, R. J.; Olmstead, . M.; Power, P. P. (2002). "Synthesis and Characterization of 2,6-Dipp2-H3C6SnSnC6H3-2,6-Dipp2 (Dipp = C6H3-2,6-Pri2): A Tin Analogue of an Alkyne". J. Am. Chem. Soc.(Communication) 124 (21): 5930–5931. doi:10.1021/ja0257164. [2]
- ^ Matthias Stender, Andrew D. Phillips, Robert J. Wright, and Philip P. Power (2002). "Synthesis and Characterization of a Digermanium Analogue of an Alkyne". Angew Chem Int ed 41 (10): 1785. doi:10.1002/1521-3757(20020517)114:10<1863::AID-ANGE1863>3.0.CO;2-I.[3]
Categories:- Silyls
- Organosilicon compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

