- Thiophosphoryl chloride
-
Thiophosphoryl chloride 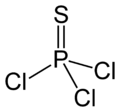
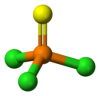
 Phosphorothioic trichlorideOther namesThiophosphoryl chloride
Phosphorothioic trichlorideOther namesThiophosphoryl chlorideIdentifiers CAS number 3982-91-0 PubChem 19883 ChemSpider 18729 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - P(=S)(Cl)(Cl)Cl
Properties Molecular formula Cl3PS Molar mass 169.4 g/mol Appearance Colorless liquid Density 1.67 g/cm3 Melting point -35 °C (987 K)
Boiling point 125 °C (1685 K)
Solubility in water Reacts Solubility Soluble in benzene, Chloroform, CS2 and CCl4. Hazards MSDS Magnesium chloride MSDS Main hazards Violent hydrolysis Flash point ?°C  chloride (verify) (what is:
chloride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Thiophosphoryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula PSCl3. [1] Thiophosphoryl chloride, PSCl3, is a fuming, colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It is synthesized from phosphorus chloride and used to thiophosphorylate organic compounds, such as to produce insecticides.
Synthesis
Thiophosporyl chloride can be generated by several reactions starting from phosphorus trichloride. The most common and practical synthesis, hence used in industrial manufacturing, is directly reacting phosphorus trichloride with excess sulfur at 180 °C. [2]
- PCl3 + S → PSCl3
Using this method, yields can be very high after purification by distillation. Catalysts can further the reaction at lower temperatures, but are not necessary. Alternatively, the reaction of phosphorus pentasulfide and phosphorus pentachloride also affords thiophosporyl chloride in yields around 70%. [3]
- 3 PCl5 + P2S5 → 5 PSCl3
Reactions
PSCl3 is soluble in benzene, carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, and carbon disulfide.[1] However, it hydrolyzes rapidly in basic or hydroxylic solutions, such as alcohols and amines, to produce thiophosphates.[2]
- PSCl3 + 4 H2O → H3PO4 + H2S + 3 HCl
- PSCl3 + H2O → HOP(S)Cl2 + HCl
PSCl3 is used to thiophosphorylate, or add P=S, organic compounds.[2] This conversion is widely applicable for amines and alcohols, as well as amino alcohols, diols, and diamines.[1] Industrially, PSCl3 is primarily used to produce insecticides, like parathion.[4]
- PSCl3 + 2 C2H5OH → (C2H5O)2PSCl + 2 HCl
- (C2H5O)2PSCl + NaOC6H4NO2 → (C2H5O)2PSOC6H4NO2 + NaCl
PSCl3 reacts with tertiary amides to generate thioamides.[1] For example:
- C6H5C(O)N(CH3)2 + PSCl3 → C6H5C(S)N(CH3)2 + POCl3
References
- ^ a b c d Spilling, C. D. "Thiophosphoryl Chloride" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis John Wiley & Sons, Weinheim, 2001. doi: 10.1002/047084289X.rt104. Article Online Posting Date: April 15, 2001.
- ^ a b c Betterman, G.; Krause, W.; Riess, G.; Hofmann, T. “Phosphorus Compounds, Inorganic” Ullman’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons: New York, 2005. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a19_527.
- ^ Martin, D. R.; Duvall, W. M. “Phosphorus (V) Sulfochloride” Inorganic Syntheses, Volume IV. McGraw-Hill, 1953. doi: 10.1002/9780470132357.ch24.
- ^ Fee, D. C.; Gard, D. R.; Yang, C. “Phosphorus Compounds” Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. John Wiley & Sons: New York, 2005. doi: 10.1002/0471238961.16081519060505.a01.pub2.
Categories:- Thiophosphoryl compounds
- Thiochlorides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
