- Cholesteatoma
-
Cholesteatoma Classification and external resources 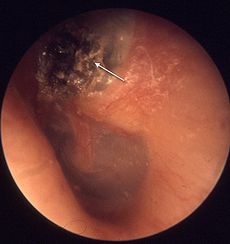
CholesteatomaICD-10 H71 ICD-9 385.32 DiseasesDB 2553 eMedicine ped/384 ent/220 MeSH D002781 Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and/or mastoid process.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
The patient may have a recurrent ear discharge. Granulation tissue and a discharge (through a marginal perforation of the ear drum) may be seen on examination. A cholesteatoma cyst consists of desquamating (peeling) layers of scaly or keratinised (horny) layers of epithelium, which may also contain cholesterol crystals. Often the debris is infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa or other bacteria or organisms.
If untreated, a cholesteatoma can eat into the three small bones located in the middle ear (the malleus, incus and stapes, collectively called ossicles), which can result in nerve deterioration, deafness, imbalance and vertigo. It can also affect and erode, through the enzymes it produces, the thin bone structure that isolates the top of the ear from the brain, as well as lay the covering of the brain open to infection with serious complications (rarely even death due to causing a brain abscess and septicemia).
Both the acquired as well as the congenital types of the disease can affect the facial nerve that extends from the brain to the face and passes through the inner and middle ear and leaves at the anterior tip of the mastoid bone, and then rises to the front of the ear and extends into the upper and lower face.
A history of ear infection or flooding of the ear during swimming should be taken seriously and investigated as cholesteatoma should be considered a possible outcome.
Common symptoms of cholesteatoma may include: Hearing loss, mucopurulent discharge from the ear (usually brown/yellow) with a strong odor, bleeding from the ear, dizziness, vertigo, balance disruption, ear ache, headaches or tinnitus. There can also be facial nerve weakness.
Causes
There are two types: congenital and acquired. Acquired cholesteatomas, which are more common, can be caused by a tear or retraction of the ear drum.
Cholesteatoma is an epidermoid cyst of the middle ear and/or mastoid. It developed as a consequence of eustachian tube dysfunction and chronic otitis media, secondary to retraction of squameous elements of the tympanic membrane into the middle ear space. Those squamous elements cause bone destruction secondary to its expanding nature and through enzymatic destruction.[1]
Less commonly the disease may be congenital, when it grows from birth behind the eardrum. Congenital cholesteatomas are more often found in the anterior aspect of the ear drum, in contrast to acquired cholesteatomas that usually arise from the pars flaccida region of the ear drum in the posterior-superior aspect of the ear drum.
Pathophysiology
The status of cholesteatomas as tumors is currently unresolved. There is some evidence to support the hypothesis that cholesteatomas are low-grade tumors.[2] However, recent studies have failed to show consistent DNA instability in cholesteatomas.[3]
Treatment
Surgery is performed to remove the sac of squamous debris and a mastoidectomy is performed. Cholesteatomas of the middle ear may be congenital and in some cases can be removed through the ear canal. The majority of cholesteatomas require that an incision be made behind the ear to expose the affected area adequately.
Prognosis
Even after careful microscopic surgical removal, 10% to 20% of cholesteatomas may recur, which then require follow-up checks and/or treatment.
References
- ^ Schwartz's principles of surgery: self assessment and board review, 8th edition, page 123 question 1
- ^ Bollmann R, Knopp U, Tolsdorff P (1991). "[DNA cytometric studies of cholesteatoma of the middle ear]". HNO 39 (8): 313–4. PMID 1938497.
- ^ Desloge RB, Carew JF, Finstad CL, Steiner MG, Sassoon J, Levenson MJ, Staiano-Coico L, Parisier SC, Albino AP (1997). "DNA analysis of human cholesteatomas". Am J Otol 18 (2): 155–9. PMID 9093669.
External links
- http://www.cholesteatoma.net - Contains Stories From People Who've Had this Condition.
- http://www.entkent.com/cholesteatoma.html - Contains loads of information on Cholesteatomas.
- http://health.groups.yahoo.com/group/cholesteatoma/ - Support group with lots of information and personal experiences.
- http://www.earsurgery.org - Ear Surgery Information Center - very informative site
Diseases of the ear and mastoid process (H60–H99, 380–389) Outer ear Middle ear and mastoid Inner ear and
central pathwaysCommon pathwayExcessive responseOtherM: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Diseases of middle ear and mastoid
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
