- Methylmalonic acid
-
Methylmalonic acid 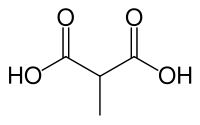 methylmalonic acidOther names2-methylpropanedioic acid
methylmalonic acidOther names2-methylpropanedioic acidIdentifiers CAS number 516-05-2 PubChem 487 MeSH Methylmalonic+acid Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(C(=O)O)C(=O)O
Properties Molecular formula C4H6O4 Molar mass 118.09 g mol−1  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Methylmalonic acid (MMA) is a dicarboxylic acid that is a C-methylated derivative of malonate.
The coenzyme A linked form of methylmalonic acid, methylmalonyl-CoA, is converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, in a reaction that requires vitamin B12 as a cofactor. In this way, it enters the Krebs cycle, and is thus part of one of the anaplerotic reactions.
Pathology
Increased methylmalonic acid levels may indicate a vitamin B12 deficiency. However, it is sensitive without being specific. MMA is elevated in 90-98% of patients with B12 deficiency. This test may be overly sensitive, as 20-25% of patients over the age of 70 have elevated levels of MMA, but 25-33% of them do not have B12 deficiency. For this reason, MMA test is not routinely recommended in the elderly. [1]
An excess is associated with methylmalonic acidemia.
MMA concentrations in blood are measured by Gas chromatographic Mass spectrometry and the expected values of MMA in healthy people are between 73-271 nmol/L. [2]
See also
References
Categories:- Dicarboxylic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
