- Dibenzothiophene
-
Dibenzothiophene 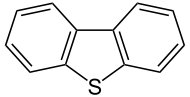
 DibenzothiopheneOther namesDiphenylene sulfide, DBT
DibenzothiopheneOther namesDiphenylene sulfide, DBTIdentifiers CAS number 132-65-0 
ChemSpider 2915 
UNII Z3D4AJ1R48 
KEGG D03777 
ChEBI CHEBI:23681 
ChEMBL CHEMBL219828 
RTECS number HQ3490550 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1ccc2c(c1)c3ccccc3s2
Properties Molecular formula C12H8S Molar mass 184.26 g/mol Appearance Colourless crystals Density 1.252 g/cm3 Melting point 97-100 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 332-333 °C
Solubility in water insol. Solubility in other solvents benzene and related Hazards R-phrases 22 S-phrases 36 Main hazards flammable Related compounds Related compounds Thiophene
anthracene
benzothiophene (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dibenzothiophene is the organosulfur compound consisting of two benzene rings fused to a central thiophene ring. It is a colourless solid that is chemically somewhat similar to anthracene. This tricyclic heterocycle, and especially its alkyl substituted derivatives, occur widely in heavier fractions of petroleum.[1]
Synthesis and reactions
Dibenzothiophene is prepared by the reaction of biphenyl with sulfur dichloride in the presence of aluminium trichloride.[2]
Reduction with lithium results in scission of one C-S bond. S-oxidation occurs to give the sulfone, which is more labile than the parent dibenzothiophene. With butyl lithium, this heterocycle undergoes stepwise lithiation at the 4- and 6- positions.
References
- ^ Teh C. Ho "Deep HDS of diesel fuel: chemistry and catalysis" Catalysis Today 2004, Volume 98, pp. 3-18. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2004.07.048
- ^ L. H. Klemm, Joseph J. Karchesy "Dibenzothiophene from biphenyl and derivatives" Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 1978, Volume 15 Issue 4, Pages 561 - 563. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570150407
Categories:- Thiophenes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
