- Trisodium citrate
-
Sodium citrate 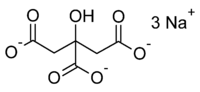 Trisodium citrate
Trisodium citrate
Trisodium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylateOther namesCitrosodine
Citric acid, trisodium salt
Sodium citrateIdentifiers CAS number 68-04-2  , 6132-04-3 (dihydrate), 6858-44-2 (pentahydrate)
, 6132-04-3 (dihydrate), 6858-44-2 (pentahydrate)RTECS number GE8300000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Na+].[Na+].[Na+]. O=C([O-])CC(O)(CC(=O)[O-])C([O-])=O
Properties Molecular formula Na3C6H5O7 Molar mass 258.06 g/mol (water free), 294.10 g/mol (dihydrate) Appearance White crystalline powder Density 1.7 g/cm3 Melting point >300 °C
hydrates lose water ca. 150 CBoiling point Decomposes
Solubility in water 42.5 g/100 ml (25 °C)[verification needed] Hazards MSDS External MSDS Main hazards Irritant Related compounds Related compounds Monosodium citrate
Disodium citrate
Calcium citrate
Citric acid citrate (verify) (what is:
citrate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Trisodium citrate has the chemical formula of Na3C6H5O7. It is sometimes referred to simply as sodium citrate, though sodium citrate can refer to any of the three sodium salts of citric acid. It possesses a saline, mildly tart flavor. For this reason, citrates of certain alkaline and alkaline earth metals (e.g. sodium and calcium citrates) are commonly known as "sour salt" (occasionally citric acid is erroneously termed sour salt).
Contents
Applications
Food
Sodium citrate is chiefly used as a food additive E331, usually for flavor or as a preservative. Sodium citrate is employed as a flavoring agent in certain varieties of club soda. Sodium citrate is common as an ingredient in Bratwurst, lemon-lime and citrus soft drinks, such as Ting, Chinotto, and some Ocean Spray juices, contributing to their tart tastes, and can also be found in such energy drinks as Rockstar and Red Bull.
Buffer
As a conjugate base of a weak acid, citrate can perform as a buffering agent or acidity regulator, resisting changes in pH. Sodium citrate is used to control acidity in some substances, such as gelatin desserts. It can be found in the mini milk containers used with coffee machines. The compound is the product of antacids, such as Alka-Seltzer, when they are dissolved in water.
Medical uses
In 1914, the Belgian doctor Albert Hustin and the Argentine physician and researcher Luis Agote successfully used sodium citrate as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions. It continues to be used today in blood collection tubes and for the preservation of blood in blood banks. The citrate ion chelates calcium ions in the blood by forming calcium citrate complexes, disrupting the blood clotting mechanism.
In 2003, Oöpik, et al., showed the use of sodium citrate (0.5 grams per kg of body weight) improved running performance over 5 km by 30 seconds.[1]
Sodium citrate is used to relieve discomfort in urinary tract infections, such as cystitis, to reduce the acidosis seen in distal renal tubular acidosis, and can also be used as an osmotic laxative.
It is used as an antacid, especially prior to anaesthesia, for caesarian section procedures to reduce the risks associated with the aspiration of gastric contents.
See also
References
- ^ V Oöpik, I Saaremets, L Medijainen, K Karelson, T Janson, S Timpmann (2003). "Effects of sodium citrate ingestion before exercise on endurance performance in well trained college runners". Br J Sports Med 37 (6): 485–489. doi:10.1136/bjsm.37.6.485. PMC 1724692. PMID 14665584. http://bjsm.bmj.com/cgi/content/abstract/37/6/485.
Categories:- Food acidity regulators
- Citrates
- Sodium compounds
- Chelating agents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
