- Monosodium citrate
-
Monosodium citrate 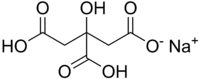 Other namessodium dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
Other namessodium dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylateIdentifiers ChemSpider 5989 ChEBI CHEBI:53258 ChEMBL CHEMBL1355 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].O=C([O-])CC(O)(C([O-])=O)CC(=O)[O-]
- InChI=1S/C6H8O7.3Na/c7-3(8)1-6(13,5(11)12)2-4(9)10;;;/h13H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12);;;/q;3*+1/p-3
Key: HRXKRNGNAMMEHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-KInChI=1/C6H8O7.3Na/c7-3(8)1-6(13,5(11)12)2-4(9)10;;;/h13H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12);;;/q;3*+1/p-3
Key: HRXKRNGNAMMEHJ-DFZHHIFOAL
Properties Molecular formula C6H7NaO7 Molar mass 214.11 g mol−1 Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Monosodium citrate, or sodium dihydrogen citrate, is an acid salt with the chemical formula NaH2C6H5O7, or C3H4OH(COOH)2COONa. Since it has two remaining open spots on the citrate anion, it is used as a relatively strong sequestrant. It is used to prevent platelet clumping in blood samples. It is one of the 3 citric acid salts.
Preparation
Monosodium citrate can be prepared by the direct reaction of sodium carbonate or bicarbonate with citric acid:
NaHCO3 (s) + C6H8O7 (aq) → NaC6H7O7 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
