- Muscular triangle
-
Muscular triangle 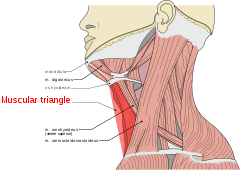
Muscular triangle 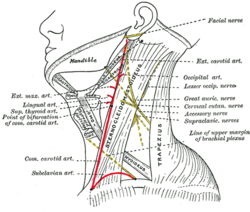
Side of neck, showing chief surface markings. (Nerves are yellow, arteries are red.) Latin trigonum musculare Gray's subject #145 563 The inferior carotid triangle (or muscular triangle), is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the Sternocleidomastoideus; above, by the superior belly of the Omohyoideus.
It is covered by the integument, superficial fascia, Platysma, and deep fascia, ramifying in which are some of the branches of the supraclavicular nerves.
Beneath these superficial structures are the Sternohyoideus and Sternothyreoideus, which, together with the anterior margin of the Sternocleidomastoideus, conceal the lower part of the common carotid artery.
This vessel is enclosed within its sheath, together with the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve; the vein lies lateral to the artery on the right side of the neck, but overlaps it below on the left side; the nerve lies between the artery and vein, on a plane posterior to both.
In front of the sheath are a few descending filaments from the ansa cervicalis; behind the sheath are the inferior thyroid artery, the recurrent nerve, and the sympathetic trunk; and on its medial side, the esophagus, the trachea, the thyroid gland, and the lower part of the larynx.
By cutting into the upper part of this space, and slightly displacing the Sternocleidomastoideus, the common carotid artery may be tied below the Omohyoideus.
Gallery
See also
External links
- SUNY Labs 25:03-0100
- SUNY Figs 25:01-00
- lesson5 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (necktriangle)
- lesson6 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- muscular+triangle at eMedicine Dictionary
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Head Neck Thorax Triangle of auscultation · axillary folds (Anterior, Posterior) · Clavipectoral triangle · Inframammary fold
Infraclavicular fossaAbdomen/pelvis regions (Epigastrium, Hypochondrium, Umbilical region, Latus, Hypogastrium, Inguinal region)
quadrants (RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, LLQ)
McBurney's point · Desjardins' point · Traube's spacePerineal General anatomy: systems and organs, regional anatomy, planes and lines, superficial axial anatomy, superficial anatomy of limbs Categories:- Human anatomy
- Head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.