- Ovarian vein
-
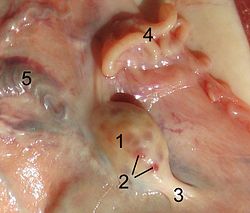
Vein: Ovarian vein Ovary of a sheep.
1. ovary
2. tertiary follicle
3. proper ovarial ligament
4. fallopian tube
5. A. and V. ovaricaLatin vena ovarica sinistra, vena ovarica dextra Drains from ovary Drains to inferior vena cava
left renal veinArtery ovarian artery The ovarian vein, the female gonadal vein, carries deoxygenated blood from its corresponding ovary to inferior vena cava or one of its tributaries. It is the female equivalent of the testicular vein, and is the venous counterpart of the ovarian artery. It can be found in the suspensory ligament of the ovary.
It a paired vein, with one supplying each ovary.
- The right ovarian vein travels through the suspensatory ligament of the ovary and generally joins the inferior vena cava.
- The left ovarian vein, unlike the right, often joins the left renal vein instead of the inferior vena cava.
Contents
Pathology
Thrombosis of ovarian vein is associated with postpartum endometritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, diverticulitis, appendicitis, and gynecologic surgery.
Additional images
See also
External links
- SUNY Labs 40:13-0103 - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Tributaries to the Inferior Vena Cava"
Veins of the abdomen and pelvis (TA A12.3.09–10, 12, GA 7.672) To azygos system IVC
(Systemic)To IVC or left renal veininferior phrenic · hepatic (central veins of liver, liver sinusoid) · suprarenal · renal · gonadal (ovarian ♀/testicular ♂, pampiniform plexus ♂) · lumbar · common iliacUnpairedposterior: iliolumbar · superior gluteal · lateral sacral
anterior: inferior gluteal · obturator · uterine ♀ (uterine plexus ♀) · vesical (vesical plexus, prostatic plexus ♂, deep of penis ♂/clitoris ♀, posterior scrotal ♂/labial ♀) · vaginal plexus/vein ♀ · middle rectal · internal pudendal (inferior rectal, bulb of penis ♂/vestibule ♀) · rectal plexusPortal vein
(Portal)DirectCategories:- Veins of the torso
- Cardiovascular system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.