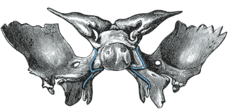
- Ossification of sphenoid
-
Until the seventh or eighth month of fetal life the body of the sphenoid consists of two parts: one in front of the tuberculum sellæ, the presphenoid, with which the small wings are continuous; the other, comprising the sella turcica and dorsum sellæ, the postsphenoid, with which are associated the great wings, and pterygoid processes.
The greater part of the bone is ossified in cartilage. There are fourteen centers in all, six for the presphenoid and eight for the postsphenoid.
Presphenoid
About the ninth week of fetal life an ossific center appears for each of the small wings (orbitosphenoids) just lateral to the optic foramen; shortly afterward two nuclei appear in the presphenoid part of the body.
The sphenoidal conchæ are each developed from a center which makes its appearance about the fifth month; at birth they consist of small triangular laminæ, and it is not until the third year that they become hollowed out and coneshaped; about the fourth year they fuse with the labyrinths of the ethmoid, and between the ninth and twelfth years they unite with the sphenoid.
Postsphenoid
The first ossific nuclei are those for the great wings (alisphenoids). One makes its appearance in each wing between the foramen rotundum and foramen ovale about the eighth week. The orbital plate and that part of the sphenoid which is found in the temporal fossa, as well as the lateral pterygoid plate, are ossified in membrane (Fawcett).
Soon after, the centers for the postsphenoid part of the body appear, one on either side of the sella turcica, and become blended together about the middle of fetal life.
Each medial pterygoid plate (except its hamulus) is ossified in membrane, and its center probably appears about the ninth or tenth week; the hamulus becomes chondrified during the third month, and almost at once undergoes ossification (Fawcett).
The medial joins the lateral pterygoid plate about the sixth month.
About the fourth month a center appears for each lingula and speedily joins the rest of the bone.
The presphenoid is united to the postsphenoid about the eighth month, and at birth the bone is in three pieces [Fig. 4]: a central, consisting of the body and small wings, and two lateral, each comprising a great wing and pterygoid process.
In the first year after birth the great wings and body unite, and the small wings extend inward above the anterior part of the body, and, meeting with each other in the middle line, form an elevated smooth surface, termed the jugum sphenoidale.
By the twenty-fifth year the sphenoid and occipital are completely fused.
Between the pre- and postsphenoid there are occasionally seen the remains of a canal, the canalis cranio-pharyngeus, through which, in early fetal life, the hypophyseal diverticulum of the buccal ectoderm is transmitted.
The sphenoidal sinuses are present as minute cavities at the time of birth (Onodi), but do not attain their full size until after puberty.
Intrinsic ligaments of the sphenoid
The more important of these are:
- the pterygospinous, stretching between the spina angularis and the lateral pterygoid plate (see cervical fascia);
- the interclinoid, a fibrous process joining the anterior to the posterior clinoid process;
- and the caroticoclinoid, connecting the anterior to the middle clinoid process.
These ligaments occasionally ossify.
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Embryology of bones, joints, and muscles (GA 2.80, TE E5.0-2) Ossification Lower limbHeadcranium: Ossification of occipital bone · Ossification of frontal bone · Ossification of temporal bone · Ossification of sphenoid · Ossification of ethmoid
facial bones: Ossification of vomer (Sutura vomerina · Foramen vomerinum · Meatus vomerinus · Fissura vomerina) · Ossification of maxilla · Ossification of mandibleOtherOther M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Skeletal system
- Tissues
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.