- Dicarbon monoxide
-
Dicarbon monoxide 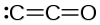

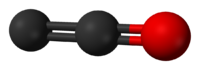 2-OxoethenylideneOther namesKetenylidene
2-OxoethenylideneOther namesKetenylideneIdentifiers CAS number 119754-08-4 
PubChem 189691 
ChemSpider 164756 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [C]=C=O
Properties Molar mass 40.02 g mol−1  monoxide (verify) (what is:
monoxide (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dicarbon monoxide (C2O) is an extremely reactive molecule that contains two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Dicarbon monoxide, covalently bonded, is a product of the photolysis of carbon suboxide.[1][2] It is closely related to CO, CO2 and C3O2, and other oxocarbons.
- C3O2 → CO + C2O
It is stable enough to observe reactions with NO and NO2.[3]
References
- ^ Bayes K. (1961). "Photolysis of Carbon Suboxide". Journal of the American Chemical Society 83 (17): 3712–3713. doi:10.1021/ja01478a033.
- ^ Anderson D. J., Rosenfeld R. N. (1991). "Photodissociation of Carbon Suboxide". Journal of Chemical Physics 94 (12): 7852–7867. doi:10.1063/1.460121.
- ^ Thweatt W. D., Erickson M. A., Hershberger J. F. (2004). "Kinetics of the CCO+NO and CCO+NO2 reactions". Journal of Physical Chemistry 108 (1): 74–79. doi:10.1021/jp0304125.
Oxocarbons Common oxides Exotic oxides Compounds derived from oxides Categories:- Oxocarbons
- Inorganic compound stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
