- Ammonium acetate
-
Ammonium acetate 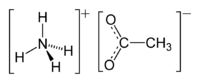
 Ammonium ethanoate
Ammonium ethanoateIdentifiers CAS number 631-61-8 
ChemSpider 11925 
UNII RRE756S6Q2 
RTECS number AF3675000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(O)C.N
Properties Molecular formula C2H3O2NH4 Molar mass 77.0825 g/mol Appearance white solid crystals
deliquescentDensity 1.17 g/cm3[1] Melting point 114 °C, 387 K, 237 °F
Boiling point decomposes
Solubility in water 148 g/100 ml (4 °C) Solubility in methanol 7.89 g/100 mL (15 °C) Structure Crystal structure orthorhombic Hazards MSDS JT Baker GHS pictograms  [2]
[2]GHS hazard statements H315, H319, H335[2] GHS precautionary statements P261, P305+351+338[2] NFPA 704  acetate (verify) (what is:
acetate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Ammonium acetate is a chemical compound with the formula CH3COONH4 (or C2H4O2.NH3 or C2H7NO2). It is a white solid, which can be derived from the reaction of ammonia and acetic acid. It is available commercially and, depending on grade, can be rather inexpensive.
Contents
Uses and distinctive properties
As the salt of a weak acid and a weak base, ammonium acetate has a number of distinctive properties.
- NH4C2H3O2 is occasionally employed as a biodegradable de-icing agent.
- It is often used with acetic acid to create a buffer solution, one that can be thermally decomposed to non-ionic products
- Ammonium acetate is useful in the Knoevenagel condensation in organic synthesis.
- It is a relatively unusual example of a salt that melts at low temperatures.
- Can be used with distilled water to make a protein precipitating reagent.
- Is often used as an aqueous buffer for ESI mass spectrometry of proteins and other molecules.
Ammonium acetate is volatile at low pressures. Because of this it has been used to replace cell buffers with non-volatile salts, in preparing samples for mass spectrometry. [3] It is also popular as a buffer for mobile phases for HPLC with ELSD detection for this reason. Other volatile salts which have been used for this include ammonium formate.
Food Additive
Ammonium acetate is also used as a food additive as an acidity regulator; INS number 264. It is approved for usage in Australia and New Zealand.[4]
Properties
CH3COONH4 is hygroscopic. It decomposes easily at elevated temperatures into acetamide.
-
- CH3COONH4 → CH3C(O)NH2 + H2O
In this reaction, a salt is converted to two molecular species, which is a relatively uncommon conversion at mild temperatures.
References
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ a b c Online Sigma Catalogue , accessdate: June 8, 2011.
- ^ Berman et al., 2008. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 19:1230-1236.
- ^ Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code"Standard 1.2.4 - Labelling of ingredients". http://www.comlaw.gov.au/Details/F2011C00827. Retrieved 2011-10-27.
Further reading
- G. Jones, Organic Reactions, 1967, volume 15, 204ff (the Knoevenagel Reaction)
Categories:- Ammonium compounds
- Acetates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


