- South African Standard Time
-
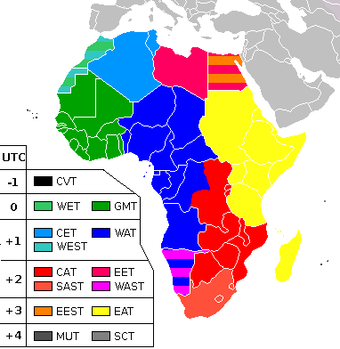 Time zones of Africa:
Time zones of Africa:
Striped colours indicate countries observing daylight savingblack UTC-1: Cape Verde Time. green UTC: Western European Time · Greenwich Mean Time. blue UTC+1: Central European Time · West Africa Time · Western European Summer Time. red UTC+2: Eastern European Time · Central Africa Time · West Africa Summer Time · South African Standard Time. yellow UTC+3: Eastern European Summer Time · East Africa Time. grey UTC+4: Mauritius Time · Seychelles Time. South African Standard Time, or SAST, is a time zone used by all of South Africa, as well as Swaziland and Lesotho. The zone is two hours ahead of UTC (UTC+2) and is the same as Central Africa Time, with Daylight saving time not being observed in either time zone. Solar noon in this time zone occurs at 30° E in SAST, effectively making Durban and Pietermaritzburg at the correct solar noon point. Everywhere west of 22°30' E effectively experiences year-round daylight saving time due to its location in true UTC+1 but still being in SAST, thus sunrise and sunset are relatively late in Cape Town compared to the rest of the country.
To illustrate, daylight hours for South Africa's western and eastern-most major cities:
1 January 1 July Cape Town 05:38–20:01 07:52–17:48 Durban 04:58–19:00 06:52–17:07 History
Prior to the 8th of February 1892 there was no uniformity of time in South Africa and local time was in use at the various towns. In 1892 a railway conference[which?] was held in Bloemfontein, and amongst the subjects discussed was the difficulty of working a railway system in the absence of a uniform time system. As an outcome the then governments of the Orange Free State, Transvaal and the Cape Colony officially adopted a uniform standard time of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)+01:30 which was defined as mean time of the 22.5º East of Greenwich.[1] On 1 March 1903 GMT+02:00 was adopted, which became the current UTC+02:00 when UTC replaced GMT for most purposes.[2][3]
Prior[when?] to the 1st of March 1903 the Colony of Natal was already using a uniform time supplied by the Natal Observatory. The observatory's local mean time being GMT+1:57.
South Africa observed a daylight saving time of GMT+3:00 from the 19th of September 1942 until 21st of March 1943.
See also
References
- ^ "Timezone change of 1892". http://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/clockchange.html?n=111&year=1892.
- ^ Mr H. E. Wood, M.Sc., Union Astronomer (1927). "1". Official Year Book of the Union of South Africa and of Basutoland, Bechuanaland Protectorate, and Swaziland. No. 10. p. 61.
- ^ "Timezone change of 1903". http://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/clockchange.html?n=111&year=1903.
 South Africa (Outline)
South Africa (Outline)History TopicsGovernment Politics Constitution · President · Political parties · Social movements · Diplomatic missions · Elections · Military · Police · Foreign relationsGeography Provinces · Districts · Municipalities · Populated places · National parks · Wildlife · Islands · Rivers · Estuaries · Lakes · Forests · Mountain rangesEconomy History · Trade · Rand · Mining industry · Agriculture · Taxation · Tourism · Transportation · Stock exchange · CompaniesSociety TopicsCrime · Demographics · Education · Health care · Languages · South African English · Media · Public holidays · Religion · SportsIssuesCrime · Gun politics · HIV/AIDS in South Africa · Human rights · Immigration · LGBT rights (Same-sex marriage) · Racism · Sexual violence · XenophobiaOther topics Time in Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Categories:- Government departments of South Africa
- Time zones
- Time in South Africa
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
