- Diesis
-
This article is about music. For other uses, see Diesis (disambiguation).
In classical music from Western culture, a diesis (difference, Greek: "leak or "escape"[1]) is either an accidental (see sharp), or a comma type of musical interval, usually defined as the difference between an octave (in the ratio 2:1) and three justly tuned major thirds (tuned in the ratio 5:4), equal to 128:125 or about 41.06 cents. In 12-tone equal temperament (on a piano for example) three major thirds in a row equal an octave, but three justly-tuned major thirds fall quite a bit narrow of an octave, and the diesis describes the amount by which they are short. For instance, an octave (2:1) spans from C to C', and three justly tuned major thirds (5:4) span from C to B♯ (namely, from C, to E, to G♯, to B♯). The difference between C-C' (2:1) and C-B♯ (125:64) is the diesis (128:125). Notice that this coincides with the interval between B♯ and C', also called a diminished second.
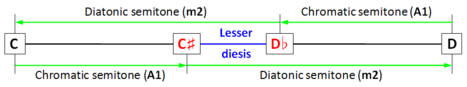
The 128:125 interval is also known as a lesser diesis, as opposed to a wider comma (648:625) known as greater diesis. As shown in the picture, in the quarter-comma meantone tuning system (a tuning system in which, by definition, major thirds are justly tuned), the diminished second coincides with the diesis.
Diesis defined in quarter-comma meantone as a diminished second (m2 − A1 ≈ 117.1 − 76.0 ≈ 41.1 cents), or an interval between two enharmonically equivalent notes (from C♯ to D♭).
 Play (help·info)
Play (help·info)Contents
Alternative definitions
In any tuning system, the deviation of an octave from three major thirds, however large that is, is typically referred to as a diminished second. The diminished second is an interval between pairs of enharmonically equivalent notes; for instance the interval between E and F♭. As mentioned above, the term diesis most commonly refers to the diminished second in quarter-comma meantone temperament. Less frequently and less strictly, the same term is also used to refer to a diminished second of any size. In third-comma meantone, the diminished second is typically denoted as a greater diesis (see below).
In quarter-comma meantone, since major thirds are justly tuned, the width of the diminished second coincides with the above mentioned value of 128:125. Notice that 128:125 is larger than a unison (1:1). This means that, for instance, C' is sharper than B♯. In other tuning systems, the diminished second has different widths, and may be smaller than a unison (e.g. C' may be flatter than B♯):
- a greater diesis above unison (648:625) for third-comma meantone temperament (see below),
- a diaschisma above unison (2048:2025) for sixth-comma,
- a schisma below unison (32768:32805) for twelfth-comma, and
- a Pythagorean comma below unison (524288:531441) for Pythagorean tuning.
In eleventh-comma meantone, the diminished second is within 1/716 (0.0014) of a cent above unison, so it closely resembles the 1:1 unison ratio of twelve-tone equal temperament.
The word diesis has also been used to describe a large number of intervals, of varying sizes, but typically around 50 cents. Philolaus used it to describe the interval now usually called a limma, that of a justly tuned perfect fourth (4:3) minus two whole tones (9:8), equal to 256:243 or about 90.22 cents. Other theorists have used it for various other intervals.
Greater and lesser diesis
Some acoustics texts use the term greater diesis[1] for the difference between an octave and four justly tuned minor thirds (tuned in the ratio 6:5), which is equal to three syntonic commas minus a schisma, equal to 648:625 or about 62.57 cents (almost one 63.16-cent division in 19 equal temperament). Being larger, this diesis was termed "greater" while the 128:125 diesis was termed "lesser".[2]
The small diesis
 Play (help·info) is 3125:3072 or approximately 28 cents.[3]
Play (help·info) is 3125:3072 or approximately 28 cents.[3]Septimal and undecimal diesis
The septimal diesis (or slendro diesis) is an interval with the ratio of 49:48
 play (help·info), which is the difference between the septimal whole tone and the septimal minor third. It is about 35.70 cents wide
play (help·info), which is the difference between the septimal whole tone and the septimal minor third. It is about 35.70 cents wideThe undecimal diesis is equal to 45:44 or about 38.91 cents, closely approximated by 31 equal temperament's 38.71 cent interval.
See also
References
- ^ a b Benson, Dave (2006). Music: A Mathematical Offering, p.171. ISBN 0521853877. Based on the technique of playing the aulos, where pitch is raised a small amount by slightly raising the finger on the lowest closed hole, letting a small amount of air "escape".
- ^ Don Michael Randel, The Harvard Dictionary of Music, Fourth Edition. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press, 2003, p. 241.
- ^ John Fonville. "Ben Johnston's Extended Just Intonation- A Guide for Interpreters", p.111, Perspectives of New Music, Vol. 29, No. 2 (Summer, 1991), pp. 106-137.
Intervals (list) Numbers in brackets are the number of semitones in the interval.
Fractional semitones are approximate.Twelve-semitone
(Western)PerfectMajorMinorAugmentedDiminishedCompoundOther systems SupermajorNeutralSubminor7-limitchromatic semitone (⅔) · diatonic semitone (1⅙) · whole tone (2⅓) · subminor third (2⅔) · supermajor third (4⅓) · harmonic (subminor) seventh (9⅔)Other intervals GroupsPythagorean comma · Pythagorean apotome · Pythagorean limma · Diesis · Septimal diesis · Septimal comma · Syntonic comma · Schisma · Diaschisma · Major limma · Ragisma · Breedsma · Kleisma · Septimal kleisma · Septimal semicomma · Orwell comma · Semicomma · Septimal sixth-tone · Septimal quarter tone · Septimal third-tone
MeasurementOthersCategories:- Commas
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.