- Diploic veins
-
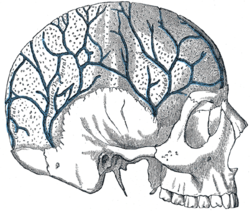
Vein: Diploic veins Veins of the diploë as displayed by the removal of the outer table of the skull. Latin venae diploicae Gray's subject #169 651 Drains from diploë The diploic veins are found in the skull, and drain the diploic space. This is found in the bones of the vault of the skull, and is the marrow-containing area of cancellous bone between the inner and outer layers of compact bone.
The diploic veins drain this area into the dural venous sinuses.
Specific diploic veins
They are usually four in number: one frontal, two temporal, and one occipital.
- (1) the frontal, which opens into the supraorbital vein and the superior sagittal sinus.
- (2) the anterior temporal, which is confined chiefly to the frontal bone, and opens into the sphenoparietal sinus and into one of the deep temporal veins, through an aperture in the great wing of the sphenoid.
- (3) the posterior temporal, which is situated in the parietal bone, and ends in the transverse sinus, through an aperture at the mastoid angle of the parietal bone or through the mastoid foramen.
- (4) the occipital, the largest of the four, which is confined to the occipital bone, and opens either externally into the occipital vein, or internally into the transverse sinus or into the confluence of the sinuses (torcular Herophili).
External links
- Diploic+veins at eMedicine Dictionary
Veins (emissary, jugular and others) of head and neck (drainage patterns can vary) (TA A12.3.04–06, GA 7.644) External jugular DirectInternal jugular Diploic/brainSuperficial cerebral veins: superior · superficial middle · inferior · inferior anastomotic (Labbé) · superior anastomotic (Trolard)
Deep cerebral veins: great · internal (basal, deep middle, superior thalamostriate)To COSTo CSTo IJVDirectBrachiocephalic DirectCategories:- Veins of the head and neck
- Cardiovascular system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.