- Cancellous bone
Infobox Anatomy
Name = PAGENAME
Latin = substantia spongiosa ossium
GraySubject = 18
GrayPage = 86
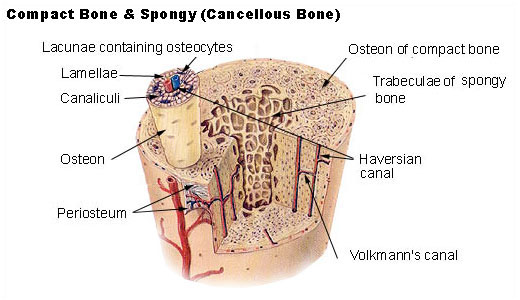
Caption = Illustration of a section through long bone, with spongy bone in its center.
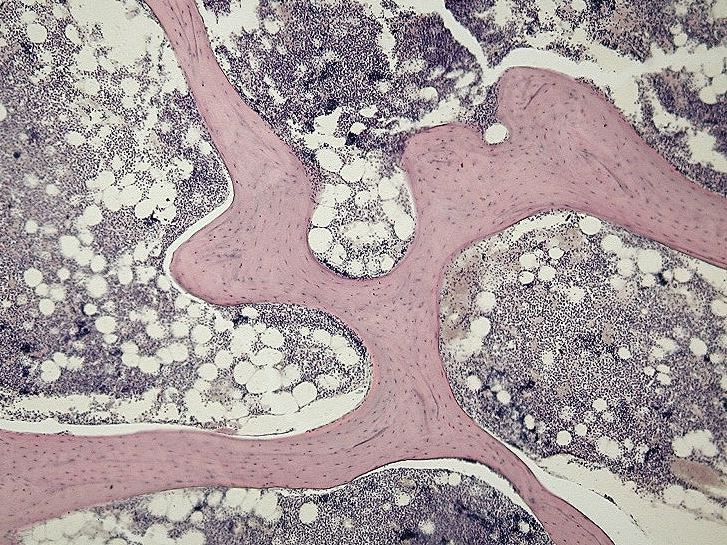
Caption2 = Light micrograph of cancellous bone, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, showing bone trabeculae (stained pink) and marrow tissue (stained blue).
Width = 350 | System =
MeshName =
MeshNumber =
DorlandsPre = s_27
DorlandsSuf = 12766958Cancellous
bone is a type ofosseous tissue with a low density and strength but very highsurface area , that fills the inner cavity of long bones. The external layer of cancellous bone contains redbone marrow where the production of blood cellular components (known ashematopoiesis ) takes place. Cancellous bone is also where most of thearteries andveins of bone organs are found.Other names include trabecular bone and spongy bone. Its Latin name is substantia spongiosa or substantia spongiosa ossium. The words "cancellous" and "trabecular" refer to the tiny, lattice-shaped that form the tissue.eMedicineDictionary|substantia+spongiosa]
ee also
*
Cortical bone , the other type of osseous tissue, which forms the hard outer layer of bone organsReferences
External links
* [http://pub.ucsf.edu/magazine/200305/genes.html Article with some info on spongy bone]
* - "Cartilage and Bone and Bone Histogenesis: trabecular, woven and lamellar bone"From Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaJump to: navigation, searchCancellous bone Illustration of a section through long bone, with spongy bone in its center. Light micrograph of cancellous bone, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, showing bone trabeculae (stained pink) and marrow tissue (stained blue). Latin substantia spongiosa ossium Gray's subject #18 86 Dorlands/Elsevier s_27/12766958 Cancellous bone (also known as trabecular, or spongy) is a type of osseous tissue with a low density and strength but very high surface area, that fills the inner cavity of long bones. The external layer of cancellous bone contains red bone marrow where the production of blood cellular components (known as hematopoiesis) takes place. Cancellous bone is also where most of the arteries and veins of bone organs are found.
The other type of osseous tissue is known as cortical bone, forming the hard outer layer of bone organs.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaJump to: navigation, searchCancellous bone Illustration of a section through long bone, with spongy bone in its center. Light micrograph of cancellous bone, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, showing bone trabeculae (stained pink) and marrow tissue (stained blue). Latin substantia spongiosa ossium Gray's subject #18 86 Dorlands/Elsevier s_27/12766958 Cancellous bone (also known as trabecular, or spongy) is a type of osseous tissue with a low density and strength but very high surface area, that fills the inner cavity of long bones. The external layer of cancellous bone contains red bone marrow where the production of blood cellular components (known as hematopoiesis) takes place. Cancellous bone is also where most of the arteries and veins of bone organs are found.
The other type of osseous tissue is known as cortical bone, forming the hard outer layer of bone organs.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
