- N-Methylformamide
-
N-Methylformamide 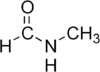
 N-MethylformamideOther namesNMF, methylformide
N-MethylformamideOther namesNMF, methylformideIdentifiers CAS number 123-39-7 
PubChem 31254 ChemSpider 28994 
KEGG C11489 
ChEBI CHEBI:7438 
ChEMBL CHEMBL9240 
RTECS number LQ3000000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=CNC
Properties Molecular formula C2H5NO Molar mass 59.067 g/mol Appearance Clear liquid Density 1.003 g/cm3, liquid Melting point -3 °C, 270 K, 27 °F
Boiling point 198-200 °C (471-473 K)
Solubility in water Miscible Refractive index (nD) 1.432 Hazards R-phrases 61-21 S-phrases 53-45 Flash point 111 °C Related compounds  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references N-Methylformamide (NMF) is a colorless, nearly odorless, organic compound with molecular formula CH3NHCHO, which is a liquid at room temperature. It is infinitely soluble in water. NMF is mainly used as a reagent in various organic syntheses with limited applications as a highly polar solvent.[1]
NMF is closely related to other formamides, notably formamide and dimethylformamide (DMF). However, industrial use and production of NMF are far less than for either of these other formamides. DMF is favored over NMF as a solvent due to its greater stability.[1] Annual production of NMF can be assumed to be significantly less than the production of either formamide (100,000 tons) or DMF (500,000 tons).[1]
Contents
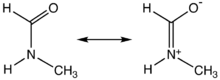
Structure and properties
Like DMF and formamide, each of the two rotamers of NMF are described by two principal resonance structures:
This description highlights the partial double bond that exists between the carbonyl carbon and nitrogen, which gives rise to a high rotational barrier. Thus, the molecule is not able to freely rotate around its main axis and the E-configuration is preferred due to steric repulsion of the larger substituents.[citation needed]
Preparation
NMF is typically prepared by allowing methylamine to react with methyl formate:[1]
- CH3NH2 + HCOOCH3 → CH3NHCHO + CH3OH
A less common alternative to this process is transamidation involving formamide:[1]
- HCONH2 + CH3NH2 → CH3NHCHO + NH3
Uses
NMF is used in specialized amidation reactions where formamide would not be suitable. These reactions can generally be categorized by the following equation:
- R-Lg + CH3NHCHO → R-NCH3CHO + H-Lg (where Lg is a leaving group)
These reactions typically proceed in high yields.[1]
NMF is the precursor to methyl isocyanide, a ligand in coordination chemistry and an intermediate in the production of some pharmaceutical compounds.[2]
References
- ^ a b c d e f Hansjörg Bipp and Heinz Kieczka "Formamides" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_001
- ^ R. E. Schuster, James E. Scott, and Joseph Casanova, Jr. (1973), "Methyl_Isocyanide", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV5P0772; Coll. Vol. 5: 772
Categories:- Amides
- Amide solvents
- Solvents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.