- Formic anhydride
-
Formic anhydride 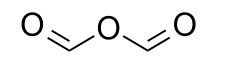 FormyloxymethanoneOther namesMethanoic anhydride
FormyloxymethanoneOther namesMethanoic anhydrideIdentifiers CAS number 1558-67-4 
PubChem 9548680 ChemSpider 7827603 
ChEBI CHEBI:36657 Beilstein Reference 1901016 Gmelin Reference 1041427 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=COC=O
Properties Molecular formula C2H2O3 Molar mass 74.04 g mol−1 Exact mass 74.000393930 g mol-1 Appearance Colorless gas Boiling point 24 °C, 297 K, 75 °F (at 20 mmHg)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Formic anhydride, also called methanoic anhydride, is a chemical compound with formula C2H2O3 or (H(C=O)-)2O. It can be viewed as the anhydride of formic acid (HCOOH).
Formic anhydride is a liquid with boiling point 24 °C at 20 mmHg.[1] It is stable in diethyl ether solution. It can be isolated by low-temperature, low-pressure distillation, but decomposes on heating above room temperature.[1] It decomposes into formic acid and carbon monoxide. [2]
Formic anhydride can be obtained by reaction of formyl fluoride with sodium formate in ether at −78 °C.[3] It can also be produced by reacting formic acid with N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide ((C6H11-N=)2C) in ether at -10 °C.[1] It can also be obtained by disproportionation of acetic formic anhydride.[4]
The decomposition of formic anhydride may be catalyzed by formic acid.[1]
Formic anhydride can be detected in the gas phase reaction of ozone with ethylene.[5] The molecule is planar in the gas phase.[1]
See also
- Acetic formic anhydride
- Acetic anhydride
- Formaldehyde
References
- ^ a b c d e G. Wu, S. Shlykov, F. S. Van Alseny, H. J. Geise, E. Sluyts, B. J. Van der Veken (1995), Formic Anhydride in the Gas Phase, Studied by Electron Diffraction and Microwave and Infrared Spectroscopy, Supplemented with Ab-Initio Calculations of Geometries and Force Fields. J. Phys. Chem., volume 99, issue 21, pages 8589–8598 doi:10.1021/j100021a022
- ^ Boogaard, A.; H. J. Geise and F. C. Mijlhoff (July 1972). "An electron diffraction investigation of the molecular structure of formic anhydride". Journal of Molecular Structure (Elsevier Science) 13 (1): 53–58. doi:10.1016/0022-2860(72)87031-5. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022286072870315. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ George A. Olah, Yashwant D. Vankar; Massoud Arvanaghi; Jean Sommer (1979), Formic Anhydride. Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed. Engl., volume 18, issue = 8, page = 614. doi:10.1002/anie.197906141.
- ^ R. Schijf, J. W. Scheeren, A. van Es, W. Stevens (1965) Mixed carboxylic acid anhydrides: IV. formic anhydride. Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, volume 84, issue 5, pages 594–596. doi:10.1002/recl.19650840510
- ^ A. Vaccani, A. Bauder and Hs. H. Günthar (1975), The Microwave Spectrum of Formic Anhydride. Abstracts of OSU International Symposium on Molecular Spectroscopy 1970-1979
Categories:- Acid anhydrides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
