- m-Xylene
-
m-Xylene 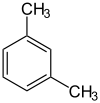
 Other namesm-Xylol
Other namesm-Xylol
1,3-DimethylbenzeneIdentifiers CAS number 108-38-3 
PubChem 7929 ChemSpider 7641 
UNII O9XS864HTE 
KEGG C07208 
ChEBI CHEBI:28488 
ChEMBL CHEMBL286727 
RTECS number ZE2275000 Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- Cc1cccc(c1)C
CC1=CC(C)=CC=C1
Properties Molecular formula C8H10 Molar mass 106.16 g/mol Appearance Colorless liquid Density 0.86 g/mL Melting point -48 °C, 225 K, -54 °F
Boiling point 139 °C, 412 K, 282 °F
Solubility in water insoluble Solubility in ethanol very soluble Solubility in diethyl ether very soluble Refractive index (nD) 1.49722 Viscosity 0.8059 cP at 0 °C
0.6200 cP at 20 °CHazards MSDS External MSDS R-phrases R10 R20 R21 R38 S-phrases S25 Main hazards Harmful or fatal if swallowed. Vapor harmful. Flammable liquid and vapor. NFPA 704 Flash point 25 °C Related compounds Related aromatic
hydrocarbonsbenzene
toluene
o-xylene
p-xyleneSupplementary data page Structure and
propertiesn, εr, etc. Thermodynamic
dataPhase behaviour
Solid, liquid, gasSpectral data UV, IR, NMR, MS  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references m-Xylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon, based on benzene with two methyl substituents.
It is an isomer of o-xylene and p-xylene. The m stands for meta, meaning the two methyl substituents are at locants 1 and 3 on the aromatic ring.
The major chemical use of metaxylene is in the manufacture of isophthalic acid, which is used as a copolymer to alter the properties of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) making PET more suitable for the manufacture of soft drinks bottles. It is also used as a raw material in the manufacture of 2,4- and 2,6-xylidine as well as a range of smaller-volume chemicals[1].
References
- ^ Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, third edition, page 9692.
Categories:- Alkylbenzenes
- Cc1cccc(c1)C
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

