- Transport in Morocco
-
Contents
Government policy
With billions of dollars committed to improving the country’s infrastructure, Morocco aims to become a world player in terms of marine transport.[citation needed] The 2008-2012 investment plan aims to invest $16.3 billion and will contribute to major projects such as the combined port and industrial complex of the Tanger-Med and the construction of a high-speed train between Tangier and Casablanca. The plan will also improve and expand the existing highway system and expand the Casablanca Mohammed V International Airport. Morocco’s transport sector is one of the kingdom’s most dynamic, and will remain so for years to come. The improvements in infrastructure will boost other sectors and will also help the country in its goal of attracting 10 million tourists by 2010.
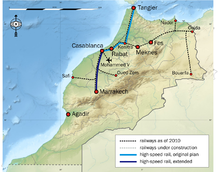
Railways
1907 km 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge, 1003 km electrified with 3 kV DC.
High-speed Lines
There are plans for several high-speed lines. Work by ONCF began in September 2011 on a first section from Tangier to Kenitra.[1] There are plans to construct two core lines, one from Tangier in the north via Marrakesh to Agadir in the south, and a second from Casablanca on the Atlantic to Oujda on the Algerian border. If all of these plans will be approved, the 1,500 kilometres of track may take until 2030 to complete at a cost of around 25 billion dirhams ($3.37 billion).
Potential speed gains are large, with travel time from Casablanca to Marrakesh down from 3 hours to 1:20, and from the capital Rabat to Tangier from 4:30 to 1:30.[2]
Other new routes
A new railway connecting Nador to the existing network at Taourirt was finished in 2010, after it had been under construction since 2007.[3]
Railway links to adjacent countries
 Algeria, but is closed since the '90s. - same gauge 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in)
Algeria, but is closed since the '90s. - same gauge 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in)
Roads
As of 2006 there were around 57625 kilometres of roads (national, regional and provincial) in Morocco,[4] and an additional 1145 kilometers of highways( July 2010 ).
Highways
Principal highways:
- A1 Rabat-Tanger (218 km)
- A2 Rabat-Fes (167 km)
- A3 Casablanca-Rabat (95 km)
- A4 Tanger-Port Tanger Med (52 km)
- A5 Casablanca bypass (37 km)
- A7 Casablanca-Marrakesh (197 km)
- A7 extension to Agadir (233 km)
- A9 Fez-Oujda (321 km)
- A11 Berrechid-Benni Mellal (172 km) (Under construction)
- National Route 1 (Morocco)
- National Route 2 (Morocco)
- National Route 3 (Morocco)
- National Route 4 (Morocco)
- National Route 5 (Morocco)
- National Route 6 (Morocco)
- National Route 7 (Morocco)
- National Route 8 (Morocco)
- National Route 9 (Morocco)
- National Route 10 (Morocco)
- National Route 11 (Morocco)
- National Route 12 (Morocco)
- National Route 13 (Morocco)
- National Route 14 (Morocco)
- National Route 15 (Morocco)
- National Route 16 (Morocco)
Major Airports
- Agadir -- Al Massira Airport: (AGA) Flights to most major European cities.
- Al Hoceima -- Cherif Al Idrissi Airport: (AHU) Flights to Brussels, Charleroi and Amsterdam
- Casablanca -- Mohammed V International Airport: (CMN) Arrivals and departures to worldwide destinations.
- Fez -- Saïss Airport: (FEZ) Flights to Europe and Casablanca
- Laayoune -- Hassan Airport: (EUN) Flights to Agadir, Casablanca, Dakhla and Las Palmas.
- Marrakech -- Menara International Airport: (RAK) Flights all major international airports in Western Europe
- Nador -- Nador International Airport: Flights to Amsterdam, Brussels, Casablanca, Cologne and Düsseldorf.
- Oujda -- Angads Airport: (OUD) Flights to Amsterdam, Casablanca, Marseille and Paris.
- Ouarzazate -- Ouarzazate Airport: (OZZ) Flights to Casablanca and Paris.
- Rabat -- Sale Airport: (RBA) Flights to Paris and Tripoli.
- Tangier -- Ibn Batouta International Airport: (TNG) Flights all major international airports in Western Europe
National airlines
- Air Arabia Maroc
- Atlas Blue
- Casa air service
- Jet4you
- Regional Air Lines
- Royal Air Maroc
- Royal Air Maroc Express
Merchant Marine
total: 35 ships (1,000 GRT or over) by type:
- cargo ship 3,
- chemical tanker 6,
- container ship 8,
- passenger/cargo ship 12,
- petroleum tanker 1,
- refrigerated cargo ship 1,
- roll-on/roll-off 4
Foreign-owned: 14 (France 13, Germany 1) (2007)
- Registered in other countries: 4 (Gibraltar)
Company maritime
- Ferrimaroc
- Tarifa-Tanger
- Comanav
- Comarit
- IMTC
- Bismillah
- Le rif-casablanca
- Ferrys Rapides du Sud
- Reduan Ferry
Sportcar
References
- ^ Ceremony launches Tanger–Casablanca high speed project, Railway Gazette, 29 September 2011.
- ^ Khaleej Times Online - Morocco plans Arab world’s first high-speed train, Khaleej Times, 15 September 2006.
- ^ The Times Atlas of the World, 2007, p. 83
- ^ CIA World Factbook
External links
 Economy of Morocco
Economy of MoroccoIndustries and sectors Overview Agriculture • Finance • Fishing • TourismEnergy Energy policy • Desertec • Renewable energy • Wind powerTechnology Information technology • Science and technology • TelecommunicationsTrade and Investment Casablanca Stock Exchange • Companies • Investment • MADEX • TradeTransportation Airlines • Autoroutes • Rail transport • ONCF • Tanger-Med port • TransportationRelated topics Regional economies Casablanca • Tangier • Western SaharaFree Trade Agreements Agadir Agreement • Euro-Med FTA • GAFTA • US-Morocco FTAGovernment policies Bank Al-Maghrib • Plan Azur • Plan Emergence • PrivatizationHistory Economic history • Falus • Trade historyCurrency: Moroccan DirhamTransport in Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the CIA World Factbook.Categories:
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the CIA World Factbook.Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.