- Deltic acid
-
Deltic acid 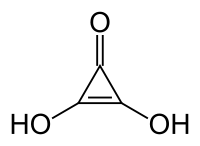
 2,3-dihydroxycycloprop-2-en-1-one
2,3-dihydroxycycloprop-2-en-1-oneIdentifiers CAS number 54826-91-4 PubChem 11679790 ChemSpider 9854518 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C1C(/O)=C1/O
- InChI=1/C3H2O3/c4-1-2(5)3(1)6/h4-5H
Key: SPXGBDTUWODGLI-UHFFFAOYAW
Properties Molecular formula C3H2O3 Molar mass 86.05 g/mol Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Deltic acid or dihydroxycyclopropenone is a chemical substance with the chemical formula C3O(OH)2. It can be viewed as a ketone and double alcohol of cyclopropene. At room temperature, it is a stable white solid, soluble in diethyl ether, that decomposes (sometimes explosively) between 140°C and 180°C, and reacts slowly with water.[1]
The synthesis of deltic acid was first described in 1975 by David Eggerding and Robert West.[2]
Contents
Derivatives
Deltate and salts
Deltic acid is considered an acid because unlike most alcohols, the hydroxyl groups lose their protons (pK1 =2.57, pK2=6.03), leaving behind the symmetric deltate anion, C3O32−.
The first deltate salts (of lithium and potassium) were described in 1976, also by Eggerding and West. Lihium deltate Li2C3O3 is a water-soluble white solid.[1] Like the other cyclic dianions with formula (CO)n2−, the deltate anion has a pronounced aromatic character which contributes to its relative stability.[1]
Analogs
An analog of the deltate anion can be obtained by replacing the three oxygen atoms (=O or -O−) by cyanoimino groups (=N-C≡N or -N=C=N−) to yield the symmetric anion C3O3(NCN)2−
3.[3]Synthesis
Deltic acid was originally obtained by photolysis of the ester bis(trimethylsilyl) squarate, which by loss of one carbonyl group (CO) from the ring was turned into bis(trimethylsilyl) deltate. Decomposition of the latter by butanol yielded deltic acid.[2]
The acid can also be prepared by reaction of silver squarate and trimethylsilyl chloride.[1][4]
Recently the deltate anion has been obtained by direct cyclotrimerization of carbon monoxide at ambient conditions. Carbon monoxide dissolved in pentane reacted with a uranium coordination compound yielding a deltate anion bound to two uranium atoms.[5]
See also
- Acetylenediol
- Croconic acid
- Rhodizonic acid
References
- ^ a b c d David Eggerding and Robert West (1976), Synthesis and properties of deltic acid (dihydroxycyclopropenone) and the deltate ion. J. American Chemical Society, volume 98, p, 3641–3644. doi:10.1021/ja00428a043.
- ^ a b David Eggerding, Robert West (1975), Synthesis of dihydroxycyclopropenone (deltic Acid). J. American Chemical Society, volume 97, issue 1, pp 207–208. doi:10.1021/ja00834a047.
- ^ Johannes Beck and Petra Krieger-Beck (2006), Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(cyanoimino)-3-triethylammonio-cyclopropenylide. Analytical Sciences, volume 22, page x239. doi:10.2116/analscix.22.x239.
- ^ M. T. Reetz, G. Neumeier, and M. Kaschube (1975), Thermische umlagerung von quadratsäure-bis(trimethylsilyl)ester. Tetrahedron Letters, page 1295. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)72653-0.
- ^ Owen T. Summerscales, F. Geoffrey N. Cloke, Peter B. Hitchcock, Jennifer C. Green, Nilay Hazari (2006), Reductive cyclotrimerization of carbon monoxide to the deltate dianion by an organometallic uranium complex. Science, volume 311, issue 5762 (10 February 2006), pp. 829 - 831. doi:10.1126/science.1121784.
Categories:- Aromatic compounds
- Ketones
- Oxocarbons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
