- Radiocontrast agent
-
Radiocontrast agents are a type of medical contrast medium used to improve the visibility of internal bodily structures in an X-ray based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) or radiography (commonly known as X-ray imaging). Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine or barium compounds.
Despite being part of radiology, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus utilizes different contrast agents. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei.
Contents
Types and uses
Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped based on its use.
Iodinated (intravascular)
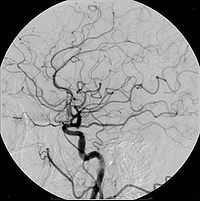 Example of iodine based contrast in cerebral angiography
Example of iodine based contrast in cerebral angiography
Iodine based contrast media are usually classified as ionic or non-ionic. Both types are used most commonly in radiology, due to its relatively harmless interaction with the body and its solubility. It is primarily used to visualize vessels, and changes in tissues on radiography and CT, but can also be used for tests of the urinary tract, uterus and fallopian tubes. It may cause the patient to feel as if he or she has urinated on himself. It also puts a metallic taste in the mouth of the patient.
Modern intravenous contrast agents are typically based on iodine. This may be bound either in an organic (non-ionic) compound or an ionic compound. Ionic agents were developed first and are still in widespread use depending on the requirements but may result in additional complications. Organic agents which covalently bind the iodine have fewer side effects as they do not dissociate into component molecules. Many of the side effects are due to the hyperosmolar solution being injected. i.e. they deliver more iodine atoms per molecule. The more iodine, the more "dense" the X-ray effect.
There are many different molecules. Some examples of organic iodine molecules are iohexol, iodixanol and ioversol. Iodine based contrast media are water soluble and harmless to the body. These contrast agents are sold as clear colorless water solutions, the concentration is usually expressed as mg I/ml. Modern iodinated contrast agents can be used almost anywhere in the body. Most often they are used intravenously, but for various purposes they can also be used intraarterially, intrathecally (as in diskography of the spine) and intraabdominally – just about any body cavity or potential space.
Iodine contrast agents are used for the following:
- Angiography (arterial investigations)
- Venography (venous investigations)
- VCUG (voiding cystourethrography)
- HSG (hysterosalpinogram)
- IVU (intravenous urography)
High osmolar (ionic)
Ionic contrast media have higher osmolarity and more side-effects, such as diatrizoic acid, Telebrix, etc.
Commonly used iodinated contrast agents Compound Name Type Iodine content Osmolality Level Ionic Diatrizoate (Hypaque 50) Monomer 300 mgI/ml 1550 High osmolar Ionic Metrizoate (Isopaque 370) Monomer 370 mgI/ml 2100 High osmolar Ionic Ioxaglate (Hexabrix) Dimer 320 mgI/ml 580 High osmolar Low osmolar (non-ionic)
Non-ionic contrast media, have lower osmolarity and tend to have fewer side-effects, such as iohexol, iopromide, iodixanol, etc.
Commonly used iodinated contrast agents Compound Name Type Iodine content Osmolality Level Non-ionic Iopamidol (Isovue 370) Monomer 370 mgI/ml 796 Low osmolar Non-ionic Iohexol (Omnipaque 350) Monomer 350 mgI/ml 884 Low osmolar Non-ionic Ioxilan (Oxilan 350) Monomer 350 mgI/ml 695 Low osmolar Non-ionic Iopromide (Ultravist 370) Monomer 370 mgI/ml 774 Low osmolar Non-ionic Iodixanol (Visipaque 320) Dimer 320 mgI/ml 290 Low osmolar Barium (gastro-intestinal)
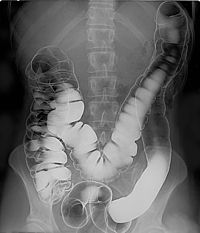
Barium sulfate is mainly used in the imaging of the digestive system. The substance exists as a water insoluble white powder that is made into a slurry with water and administered directly into the gastrointestinal tract.
- Barium enema (large bowel investigation) and DCBE (double contrast barium enema)
- Barium swallow (oesophagael investigation)
- Barium meal (stomach investigation) and double contrast barium meal
- Barium follow through (stomach and small bowel investigation)
- CT pneumocolon / virtual colonoscopy
Barium sulfate, an insoluble white powder is typically used for enhancing contrast in the GI tract. Depending on how it is to be administered the compound is mixed with water, thickeners, de-clumping agents, and flavourings to make the contrast agent. As the barium sulfate doesn't dissolve, this type of contrast agent is an opaque white mixture. It is only used in the digestive tract; it is usually swallowed or administered as an enema. After the examination, it leaves the body with the feces.
Air
As in the picture on the left where both air and barium are used together (hence the term "double-contrast" barium enema) air can be used as a contrast material because it is less radio-opaque than the tissues it is defining. In the picture it highlights the interior of the colon. An example of a technique using purely air for the contrast medium is an air arthrogram where the injection of air into a joint cavity allows the cartilage covering the ends of the bones to be visualised.
Other
An older type of contrast agent, Thorotrast was based on thorium dioxide, but this was abandoned since it turned out to be carcinogenic.
Adverse effects
Modern iodinated contrast agents are safe drugs; adverse reactions exist but they are uncommon. The major side effects of radiocontrast are anaphylactoid reactions and contrast-induced nephropathy.
Anaphylactoid reactions
Anaphylactoid reactions occur rarely,[1][2][3] but can occur in response to injected as well as oral and rectal contrast and even retrograde pyelography.
They are similar in presentation to anaphylactic reactions, but are not caused by an IgE-mediated immune response. Patients with a history of contrast reactions, however, are at increased risk of anaphylactoid reactions.[4][5]
Pretreatment with corticosteroids has been shown to decrease the incidence of adverse reactions.[6][7]
Anaphylactoid reactions range from urticaria and itching, to bronchospasm and facial and laryngeal edema. For simple cases of urticaria and itching, Benadryl (diphenhydramine) oral or IV is appropriate. For more severe reactions, including bronchospasm and facial or neck edema, albuterol inhaler, or subcutaneous or IV epinephrine, plus diphenhydramine may be needed. If respiration is compromised, an airway must be established prior to medical management.
Contribution of seafood and other allergies
There are no true allergies against iodine. Suspicion of seafood "allergy" is not a sufficient contraindication to the use of iodinated contrast material. While iodine levels in seafood are higher than in non-seafood items, the consumption of the latter exceeds that of the former by far and there is no evidence that the iodine content of seafood is related to reactions to seafood.[8] Available data suggest that seafood allergy increases the risk of a contrast-mediated reaction by approximately the same amount as allergies to fruits or those with asthma.[9] In other words, over 85% of patients with seafood allergies will not have an adverse reaction to iodinated contrast.[8] Finally, there is no evidence that adverse skin reactions to iodine-containing topical antiseptics (e.g., povidone-iodine) are of any specific relevance to administration of I.V. contrast material.[8][10]
Contrast-induced nephropathy
Main article: Contrast-induced nephropathyContrast-induced nephropathy is defined as either a greater than 25% increase of serum creatinine or an absolute increase in serum creatinine of 0.5 mg/dL.[11]
Drug interactions
It has been recommended[12] that metformin, an oral antidiabetic agent, be stopped for 48 hours following the intravascular administration of contrast media and that the use of metformin not be resumed until renal function has been shown to be normal. The reasoning is that if the contrast medium causes kidney failure (as happens rarely) and the person continues to take metformin (which is normally excreted by the kidneys), there may be a toxic accumulation of metformin, increasing the risk of lactic acidosis, a dangerous complication.
However, guidelines published by the Royal College of Radiologists suggest this is not as important for patients who receive less than 100 ml of contrast media and have normal renal function. If renal impairment is found before administration of the contrast, metformin should be stopped 48 hours before and after the procedure.[13]
References
- ^ Karnegis JN, Heinz J (1979). "The risk of diagnostic cardiovascular catheterization". Am Heart J 97 (3): 291–7. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(79)90427-7. PMID 420067.
- ^ Lasser EC, Berry CC, Talner LB, Santini LC, Lang EK, Gerber FH, Stolberg HO (1987). "Pretreatment with corticosteroids to alleviate reactions to intravenous contrast material". N Engl J Med 317 (14): 845–9. doi:10.1056/NEJM198710013171401. PMID 3627208.
- ^ Greenberger PA, Patterson R, Tapio CM (1985). "Prophylaxis against repeated radiocontrast media reactions in 857 cases. Adverse experience with cimetidine and safety of beta-adrenergic antagonists". Arch Intern Med 145 (12): 2197–200. doi:10.1001/archinte.145.12.2197. PMID 2866755.
- ^ Greenberger PA, Patterson R (1988). "Adverse reactions to radiocontrast media". Prog Cardiovasc Dis 31 (3): 239–48. doi:10.1016/0033-0620(88)90017-5. PMID 3055068.
- ^ Lang DM, Alpern MB, Visintainer PF, Smith ST (1993). "Elevated risk of anaphylactoid reaction from radiographic contrast media is associated with both beta-blocker exposure and cardiovascular disorders". Arch Intern Med 153 (17): 2033–40. doi:10.1001/archinte.153.17.2033. PMID 8102844.
- ^ Lasser EC, Berry CC, Talner LB, Santini LC, Lang EK, Gerber FH, Stolberg HO (1988). "Protective effects of corticosteroids in contrast material anaphylaxis". Invest Radiol 23 Suppl 1: S193–4. PMID 3058630.
- ^ Wittbrodt ET, Spinler SA (1994). "Prevention of anaphylactoid reactions in high-risk patients receiving radiographic contrast media". Ann Pharmacother 28 (2): 236–41. PMID 8173143.
- ^ a b c Coakley F, Panicek D (1997). "Iodine allergy: an oyster without a pearl?". AJR Am J Roentgenol 169 (4): 951–2. PMID 9308442.
- ^ Shehadi W (1975). "Adverse reactions to intravascularly administered contrast media. A comprehensive study based on a prospective survey". Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 124 (1): 145–52. PMID 1170768.
- ^ van Ketel W, van den Berg W (1990). "Sensitization to povidone-iodine". Dermatol Clin 8 (1): 107–9. PMID 2302848.
- ^ Barrett BJ, Parfrey PS (2006). "Clinical practice. Preventing nephropathy induced by contrast medium". N. Engl. J. Med. 354 (4): 379–86. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp050801. PMID 16436769.
- ^ http://www.amershamhealth-us.com/medpro/clinref/glucophage.html[dead link]
- ^ Thomsen HS, Morcos SK, and members of the Contrast Media Safety Committee of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology. Contrast media and Metformin. Guidelines to distinguish the risk of lactic acidosis in non-insulin dependent diabetics after administration of contrast media.European Radiology, 1999; 9: 738-740.
See also
Contrast media (V08) X-ray and CT Iodinated,
Water solubleNephrotropic,
high osmolarDiatrizoic acid# • Metrizoic acid • Iodamide • Iotalamic acid • Ioxitalamic acid • Ioglicic acid • Acetrizoic acid • Iocarmic acid • Methiodal • DiodoneNephrotropic,
low osmolarHepatotropicIodoxamic acid • Iotroxic acid • Ioglycamic acid • Adipiodone • Iobenzamic acid • Iopanoic acid • Iocetamic acid • Sodium iopodate • Tyropanoic acid • Calcium iopodateIodinated,
Water insolubleEthyl esters of iodised fatty acids • Iopydol • Propyliodone • Iofendylate • LipiodolNon-iodinatedMRI ParamagneticGadolinium-based: Gadobenic acid • Gadobutrol • Gadodiamide • Gadofosveset • Gadolinium • Gadopentetic acid • Gadoteric acid • Gadoteridol • Gadoversetamide • Gadoxetic acid
Other: Ferric ammonium citrate • MangafodipirFerumoxsil • Ferristene • Iron oxide, nanoparticlesOtherPerflubronUltrasound Microspheres of human albumin • Microparticles of galactose • Perflenapent • Microspheres of phospholipids • Sulfur hexafluorideCategories:- Radiocontrast agents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.