- Coda (music)
-
Coda (Italian for "tail", plural code) is a term used in music in a number of different senses, primarily to designate a passage that brings a piece (or one movement thereof) to a conclusion. Technically, it is an expanded cadence, and occurs at the end of a composition and traditionally brings it to a satisfying conclusion. A coda may be as simple as a few measures, or as complex as an entire section.[2]
Contents
Coda as a section of a movement
Many classical era, especially Mozart pieces, have Code, such as "C Major Sonata" on the last movement and "Rondo Alla Turca (Turkish March)" A Major Last movement of Sonata 11. In "Rondo Alla Turca", it is generally a syncopated section with lots of A Major Chords. Coda literally translates from Italian as "tail" and it is the tail (end section) of the piece.
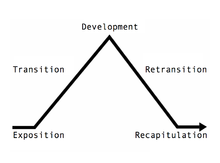 Sonata form as a dramatic pyramid. For example, the coda may follow the recapitulation (and thus come after the pyramid), or may be the last part of the recapitulation (and thus would be like the point of the arrow).
Sonata form as a dramatic pyramid. For example, the coda may follow the recapitulation (and thus come after the pyramid), or may be the last part of the recapitulation (and thus would be like the point of the arrow).
The presence of a coda as a structural element in a music movement is especially clear in works written in particular musical forms. In a sonata form movement, the recapitulation section will, in general, follow the exposition in its thematic content, while adhering to the home key. The recapitulation often ends with a passage that sounds like a termination, paralleling the music that ended the exposition; thus, any music coming after this termination will be perceived as extra material, i.e., as a coda. In works in variation form, the coda occurs following the last variation and will be very noticeable as the first music not based on the theme.
Codas were commonly used in both sonata form and variation movements during the Classical era. One of the ways that Beethoven extended and intensified Classical practice was to expand the coda sections, producing a final section sometimes of equal musical weight to the foregoing exposition, development, and recapitulation sections and completing the musical argument. For one famous example, see Symphony No. 8 (Beethoven).[3]
Musical purpose
Charles Burkhart suggests that the reason codas are common, even necessary, is that, in the climax of the main body of a piece, a "particularly effortful passage", often an expanded phrase, is often created by "working an idea through to its structural conclusions" and that, after all this momentum is created, a coda is required to "look back" on the main body, allow listeners to "take it all in", and "create a sense of balance."[4]
In music notation
In music notation, the coda symbol, which resembles a set of crosshairs, is used as a navigation marker, similar to the dal Segno sign. It is used where the exit from a repeated section is within that section rather than at the end. The instruction "To Coda" indicates that, upon reaching that point during the final repetition, the performer is to jump immediately to the separate section headed with the coda symbol. For example, this can be used to provide a special ending for the final verse of a song.
This symbol is encountered mainly in modern music, not works by classical composers such as Haydn or Mozart.
Cauda
Cauda, the Latin root of coda, is used in the study of conductus of the 12th and 13th centuries. The cauda was a long melisma on one of the last syllables of the text, repeated in each strophe. Conducti were traditionally divided into two groups, conductus cum cauda and conductus sine cauda (Latin: "conductus with cauda", "conductus without cauda"), based on the presence of the melisma. Thus, the cauda provided a conclusionary role, also similar to the modern coda.
Codetta
Codetta (Italian for "little tail," the diminutive form) has a similar purpose to the coda, but on a smaller scale, concluding a section of a work instead of the work as a whole. A typical codetta concludes the exposition and recapitulation sections of a work in sonata form, following the second (modulated) theme, or the closing theme (if there is one). Thus, in the exposition, it usually appears in the secondary key, but, in the recapitulation, in the primary key. The codetta ordinarily closes with a perfect cadence in the appropriate key, confirming the tonality. If the exposition is repeated, the codetta is also, but sometimes it has its ending slightly changed, depending on whether it leads back to the exposition or into the development sections.
Codas in popular music
Many songs in rock and other genres of popular music have sections identifiable as codas. A coda in these genres is sometimes referred to as an "outro" and in jazz and modern church music as a "tag".
See also
- Repeat sign
- Da capo
- Dal segno
- Epilogue
- Transition (music)
- Fade out
References
- ^ Benward & Saker (2009). Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II, p.151. Eighth Edition. ISBN 978-0-07-310188-0.
- ^ Benward & Saker (2009), p.355.
- ^ For discussion of this coda, and of codas in general, see Rosen, Charles (1988) Sonata Forms, 2nd edition. New York: Norton.
- ^ Burkhart, Charles. "The Phrase Rhythm of Chopin's A-flat Major Mazurka, Op. 59, No. 2" in Stein, Deborah (2005). Engaging Music: Essays in Music Analysis, p.12. New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-517010-5.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.Musical form Arch form · Binary form · Coda · Conclusion · Exposition · Movement · Development · Recapitulation · Rondo · Section · Sonata form · Sonata rondo form · Strophic form · Ternary form · Through-composed · Transition · Variation
Musical notation and development Staff 
Notes Accidental (Flat · Natural · Sharp) · Dotted note · Grace note · Note value (Beam · Note head · Stem) · Pitch · Rest · Tuplet · Interval · Helmholtz pitch notation · Letter notation · Scientific pitch notation
Articulation Development Coda · Exposition · Harmony · Melody · Motif · Ossia · Recapitulation · Repetition · Rhythm (Beat · Meter · Tempo) · Theme · Tonality · Atonality
Related Categories:- Auxiliary members
- Italian loanwords
- Musical notation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.