- Helmholtz pitch notation
-
Helmholtz pitch notation is a musical system for naming notes of the Western chromatic scale. Developed by the German scientist Hermann von Helmholtz, it uses a combination of upper and lower case letters (A to G),[1] and the sub- and super-prime symbols ( ͵ ′ ) to describe each individual note of the scale. It is one of two formal systems for naming notes in a particular octave, the other being scientific pitch notation.[2]
Contents
History
Helmholtz developed this system in order to accurately define pitches in his classical work on acoustics Die Lehre von den Tonempfindungen als physiologische Grundlage für die Theorie der Musik (1863) translated into English by A. J. Ellis as On the Sensations of Tone (1875).[3] The system is widely used by musicians across Europe. Once also widely used by scientists and doctors when discussing the scientific and medical aspects of sound in relation to the auditory system, it has now largely been replaced in scientific and medical contexts by scientific pitch notation.[4]
Usage
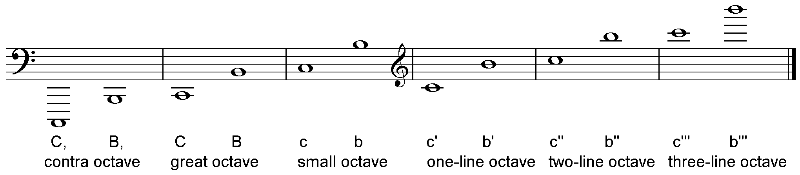
The Helmholtz scale always starts on the note C and ends at B (C, D, E, F, G, A, B). The note C is shown in different octaves by using upper-case letters for low notes, and lower-case letters for high notes, and adding sub-primes and primes in the following sequence: C͵͵ C͵ C c c′ c″ c″′ (or ͵͵C ͵C C c c′ c″ c″′) and so on.
Middle C is designated c′, therefore the octave upwards from middle C is c'-b'.
Each octave may also be given a name based on the "German method" (see below). For example, the octave from c′–b′ is called the one-line octave.[2]
Variations
- The English multiple C notation uses repeated Cs in place of the sub-prime symbol. Therefore C͵ is rendered as CC.[4]
- The German method replaces the "prime" with a horizontal bar above the letter.[4] While this method looks very similar to ABC notation, currently used mainly in the notation of folk music, differences do exist.
- Scientific pitch notation is a similar system that replaces primes and sub-primes with integers. Hence C4 in scientific notation is c′ (middle C).
Staff representation
This diagram gives examples of the lowest and highest note in each octave, giving their name in the Helmholtz system, and the "German method" of octave nomenclature. (The octave below the contra octave is known as the sub-contra octave).
See also
References
- ^ The letter B is used in Germany to designate a standard B flat, H is used for B natural.
- ^ a b Schmidt-Jones, Catherine Octaves and the Major-Minor Tonal System. Retrieved on 3 August 2007.
- ^ The Concise Grove Dictionary of Music: Hermann von Helmholtz, Oxford University Press (1994), Answers.com. Retrieved 3 August 2007.
- ^ a b c Blood, Brian. "music theory online: staffs, clefs & pitch notation". Retrieved on 2 August 2007.
External links
Musical notation and development Staff 
Notes Accidental (Flat · Natural · Sharp) · Dotted note · Grace note · Note value (Beam · Note head · Stem) · Pitch · Rest · Tuplet · Interval · Helmholtz pitch notation · Letter notation · Scientific pitch notation
Articulation Development Coda · Exposition · Harmony · Melody · Motif · Ossia · Recapitulation · Repetition · Rhythm (Beat · Meter · Tempo) · Theme · Tonality · Atonality
Related Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.