- Musical development
-
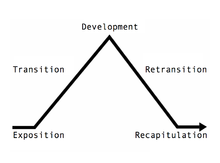 Sonata form as a dramatic pyramid featuring the three main sections: the exposition, the development, and the recapitulation.
Sonata form as a dramatic pyramid featuring the three main sections: the exposition, the development, and the recapitulation.
In European classical music, musical development is a process by which a musical idea is communicated in the course of a composition. It refers to the transformation and restatement of initial material, and is often contrasted with musical variation, which is a slightly different means to the same end. Development is carried out upon portions of material treated in many different presentations and combinations at a time, while variation depends upon one type of presentation at a time.[2]
In this process, certain central ideas are repeated in different contexts or in altered form so that the mind of the listener consciously or unconsciously compares the various incarnations of these ideas. Listeners may apprehend a "tension between expected and real results" (see irony), which is one "element of surprise" in music. This practice has its roots in counterpoint, where a theme or subject might create an impression of a pleasing or affective sort, but would go on to further delight the mind as its contrapuntal capabilities are gradually unveiled.
The musical form which traditionally exploits development to the fullest is the sonata form. In this form there is a section after the exposition and before the recapitulation which is called the development section, where material from the exposition section is developed. In some older texts the development section of a sonata may be referred to as "free fantasia."
See also
References
- ^ Benward & Saker (2009), Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II, p.138-39. Eighth Edition. ISBN 978-0-07-310188-0.
- ^ Wennerstrom, Mary (1975). "Form in Twentieth-Century Music" (chap. 1), Aspects of Twentieth-Century Music. Wittlich, Gary (ed.). Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall. ISBN 0-13-049346-5.
Musical notation and development Staff 
Notes Accidental (Flat · Natural · Sharp) · Dotted note · Grace note · Note value (Beam · Note head · Stem) · Pitch · Rest · Tuplet · Interval · Helmholtz pitch notation · Letter notation · Scientific pitch notation
Articulation Development Coda · Exposition · Harmony · Melody · Motif · Ossia · Recapitulation · Repetition · Rhythm (Beat · Meter · Tempo) · Theme · Tonality · Atonality
Related Musical form Arch form · Binary form · Coda · Conclusion · Exposition · Movement · Development · Recapitulation · Rondo · Section · Sonata form · Sonata rondo form · Strophic form · Ternary form · Through-composed · Transition · Variation
Categories:- Musical techniques
- Formal sections in music analysis
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

