- Yunis–Varon syndrome
-
Yunis Varon syndrome Classification and external resources ICD-10 Q87.8 OMIM 216340 DiseasesDB 33830 Yunis-Varon syndrome (YVS), also called cleidocranial dysplasia with micrognathia, absent thumbs and distal aphalangia,[1][2] is an extremely rare[3] autosomal recessive[4] multisystem congenital disorder[5] which affects the skeletal system, ectodermal tissue, heart and respiratory system.
Contents
Characteristics
Features of YVS include growth retardation before and after birth, defective growth of the bones of the skull along with complete or partial absence of the shoulder blades and characteristic facial features.[3][6] Additional symptoms may include abnormalities of the fingers and/or toes.[6][7] In most cases, infants with this disorder experience severe feeding problems and respiratory difficulties. In addition, affected infants may have heart defects.
Genetics
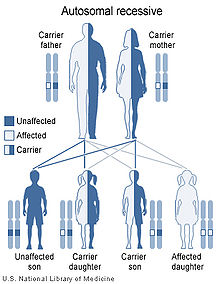 Yunis-Varon syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Yunis-Varon syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
This syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.[4][8]
Epidemiology
YVS has been described relatively recently in the 1980s and since then less than 15 cases have been reported around the world. Many of the infants did not survive beyond one year of age.[7][8]
References
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 216340
- ^ Kulkarni ML, Vani HN, Nagendra K, et al. (2006). "Yunis-Varon syndrome" (PDF). Indian J Pediatr 73 (4): 353–355. doi:10.1007/BF02825832. PMID 16816498. http://medind.nic.in/icb/t06/i4/icbt06i4p353.pdf.
- ^ a b Christie, J; Sacks, S; Decorato, D; Bergasa, Nv (Sep 1999). "Atrophy of the left lobe of the liver and anomalous hepatic vessel in a patient with Yunis-Varon syndrome". Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 29 (2): 210–211. doi:10.1097/00004836-199909000-00025. PMID 10478891.
- ^ a b Basel-Vanagaite, L; Kornreich, L; Schiller, O; Yacobovich, J; Merlob, P (Feb 2008). "Yunis-Varon syndrome: further delineation of the phenotype". American journal of medical genetics. Part A 146A (4): 532–537. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32135. PMID 18203163.
- ^ Yunis Varon Syndrome
- ^ a b "Yunis-Varon syndrome". Disease Information from NORD, National Organization for Rare Disorders, Inc.. http://www.rarediseases.org/search/rdbdetail_abstract.html?disname=Yunis%20Varon%20Syndrome.
- ^ a b Bhatia S, Holla RG (Apr 2005). "Yunis-Varon syndrome" (PDF). Indian Pediatr 42 (4): 373–375. PMID 15876600. http://www.indianpediatrics.net/apr2005/373.pdf.
- ^ a b Yunis, E; Varón, H (July 1980). "Cleidocranial dysostosis, severe micrognathism, bilateral absence of thumbs and first metatarsal bone, and distal aphalangia: a new genetic syndrome" (Free full text). American journal of diseases of children (1960) 134 (7): 649–53. ISSN 0002-922X. PMID 7395825. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/headandbrainmalformations.html.
External links
- Yunis-Varon syndrome; Cleidocranial dysplasia, micrognathia, absent thumbs, & distal aphalangia at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
Congenital abnormality · multiple abnormalities (Q87, 759.7) Craniofacial Short stature 1q21.1 deletion syndrome · Aarskog–Scott syndrome · Cockayne syndrome · Cornelia de Lange Syndrome · Dubowitz syndrome · Noonan syndrome · Robinow syndrome · Silver–Russell syndrome · Seckel syndrome · Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome-Turner syndromeLimbs Overgrowth Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl Bardet–Biedl syndrome · Laurence-Moon syndromeCombined/other,
known locus3 (Zimmerman-Laband syndrome) · 4/13 (Fraser syndrome) · 8 (Branchio-oto-renal syndrome) · 12 (Keutel syndrome, Timothy syndrome) · 15 (Marfan syndrome) · 19 (Donohue syndrome)Categories:- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Rare diseases
- Syndromes
- Genetic disorders with OMIM but no gene
- Genetic disorder stubs
- Disease stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
