- Classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages
-
Below is a list of different classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages. Language families represented include:
Contents
Macrofamilies
Austric links the languages of Southeast Asia apart from Sino-Tibetan. Sagart proposes instead Sino-Austronesian, linking Austronesian and Sino-Tibetan; Starosta proposed a family called East Asian which covered both this and Austric. Genetic similarities between the peoples of East and Southeast Asian languages have lead some to speculate about "Haplogroup O" languages. In a different direction, the Dené–Caucasian hypothesis links Sino-Tibetan to languages of Siberia (Dene–Yeniseian) and the Caucasus.
Proto-languages
Main article: List of proto-languages- Proto-Austronesian [1] [2]
- Proto-Kradai language
- Proto-Austro-Asiatic language
- Proto-Mon–Khmer [15]
- Proto-Munda language
- Proto-Sino-Tibetan language
- Old Chinese language [16]
- Proto-Tibeto-Burman [17]
- Proto-Hmong–Mien [18]
Comparison
The following table compares the phonemic inventories of various recently reconstructed proto-languages of Southeast Asia.
Comparison of Proto-languages Proto-language Proto-Kra Proto-Tai Proto-Hlai Proto-S. Kradai Proto-Austronesian Proto-Tibeto-Burman Proto-Mon–Khmer Source Ostapirat (2000) Pittayaporn (2009)[1] Norquest (2007)[2] Norquest (2007)[2] Blust (2009)[3] Matisoff (2003)[4] Shorto (2006)[5] Consonants 32 33-36 32 28-29 25 23 21 Vowels 6 7 4-5 5-7 4 5-6 7 Diphthongs 4 5 – 1+ 4 2+ 3 Consonantal finals 7 10-11 – – – 6 – Vowel length
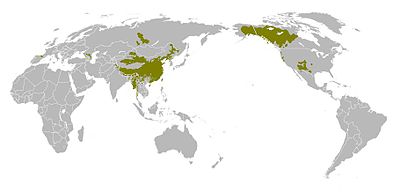
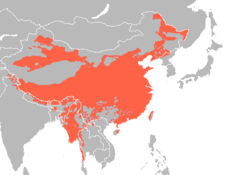
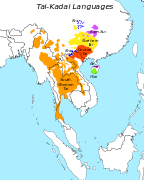
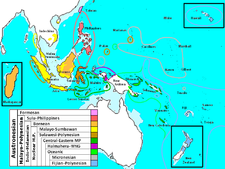
contrastNo Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes Maps of language families
See also
- Category:Southeast Asian language scholars
- Category:Austronesianists
Notes
- ^ Pittayaporn, Pittayawat. 2009. The Phonology of Proto-Tai. Ph.D. dissertation. Department of Linguistics, Cornell University.
- ^ a b Norquest, Peter K. 2007. A Phonological Reconstruction of Proto-Hlai. Ph.D. dissertation. Tucson: Department of Anthropology, University of Arizona.
- ^ Blust, Robert A. 2009. The Austronesian Languages. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. ISBN 0858836025, 978-0858836020.
- ^ Matisoff, James. 2003. Handbook of Proto-Tibeto-Burman: System and Philosophy of Sino-Tibetan Reconstruction. University of California publications in linguistics, v. 135. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- ^ Shorto, Harry L., et. al. 2006. A Mon–Khmer Comparative Dictionary. Canberra: Australian National University. Pacific Linguistics. ISBN 0-85883-570-3.
Categories:- Languages of Southeast Asia
- Languages of China
- Language classification
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.