- epsilon-Viniferin
-
ε-Viniferin 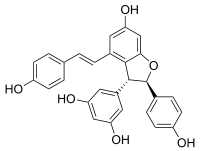 5-[(2R,3R)-6-Hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-[(E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-3-yl]benzene-1,3-diolOther namesViniferin; epsilon-Viniferin; (-)-epsilon-Viniferin
5-[(2R,3R)-6-Hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-[(E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-3-yl]benzene-1,3-diolOther namesViniferin; epsilon-Viniferin; (-)-epsilon-ViniferinIdentifiers CAS number 62218-08-0 
PubChem 5281728 ChemSpider 4445043 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1224875 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1=CC(=CC=C1C=CC2=CC(=CC3=C2C(C(O3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)O)C5=CC(=CC(=C5)O)O)O)O
- InChI=1S/C28H22O6/c29-20-7-2-16(3-8-20)1-4-18-11-24(33)15-25-26(18)27(19-12-22(31)14-23(32)13-19)28(34-25)17-5-9-21(30)10-6-17/h1-15,27-33H/b4-1+/t27-,28+/m1/s1

Key: FQWLMRXWKZGLFI-YVYUXZJTSA-N
InChI=1/C28H22O6/c29-20-7-2-16(3-8-20)1-4-18-11-24(33)15-25-26(18)27(19-12-22(31)14-23(32)13-19)28(34-25)17-5-9-21(30)10-6-17/h1-15,27-33H/b4-1+/t27-,28+/m1/s1
Key: FQWLMRXWKZGLFI-YVYUXZJTBS
Properties Molecular formula C28H22O6 Molar mass 454.47 g mol−1 Exact mass 454.141638 u  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references ε-Viniferin is a naturally occurring polyphenol, belonging to the stilbenoids family. It is found in grapevines,[1] in wines,[2] and in the Oriental medicinal plant Vitis coignetiae.
It is a resveratrol dimer.
Glycosides
Diptoindonesin A is a C-glucoside of ε-viniferin.
References
- ^ A new class of phytoalexins from grapevines. P. Langcake and R. J. Pryce, Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 1977, Volume 33, Number 2, pp. 151-152, doi:10.1007/BF02124034 PMID 844529
- ^ Vitrac, Xavier; Bornet, Aurélie; Vanderlinde, Regina; Valls, Josep; Richard, Tristan; Delaunay, Jean-Claude; Mérillon, Jean-Michel; Teissédre, Pierre-Louis (2005). "Determination of Stilbenes (δ-viniferin, trans-astringin, trans-piceid, cis- and trans-resveratrol, ε-viniferin) in Brazilian Wines.". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 53 (14): 5664–9. doi:10.1021/jf050122g. PMID 15998130.
External links
Stilbenoids Combretastatin | Combretastatin A-1 | Combretastatin A-4 | Combretastatin B-1 | Piceatannol | Pinosylvin | Pterostilbene | ResveratrolGlycosides Oligomeric forms Ampelopsin A | Ampelopsin E | Carasinol B | Diptoindonesin C | Diptoindonesin F | Flexuosol A | Gnetin H | Hemsleyanol D | Kobophenol A | Laetevirenol A, B, C, D and E | Vaticanol B | Viniferal | Tetramers : Laetevirenol F and GOligomers of resveratrolDimers : ε-viniferin, Parthenocissin A, Quadrangularin A, Pallidol and Amurensin A | Trimers : α-viniferin, Laevifonol (an ε-viniferin-ascorbic acid hybrid compound), trans-diptoindonesin B | Tetramers : Hopeaphenol | Vitisins A, B and COligomeric forms glycosides Misc Synthetic Stilbenoid drugsThis article about a natural phenol is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
